Prognostic effects of the expression of inhibitor of DNA-binding family members on patients with lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 32934711
- PMCID: PMC7471671
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2020.12004
Prognostic effects of the expression of inhibitor of DNA-binding family members on patients with lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
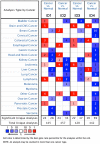
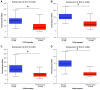
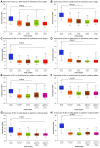
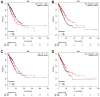
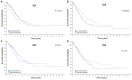
The basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors are negatively regulated by inhibitor of DNA-binding (ID) proteins. Several studies have demonstrated that ID family proteins are dysregulated in a variety of cancer types, including in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). In current study, the prognostic value of ID family members was evaluated by investigating publicly accessible databases, including Oncomine, Kaplan-Meier plotter, UALCAN and the Human Protein Atlas. It was observed that the mRNA expression of all ID members was downregulated in LUAD tumor tissues compared with those in normal tissues according to the Oncomine and UALCAN databases. Additionally, increased mRNA expression levels of ID2 and ID1 were associated with improved and poorer survival time, respectively. Notably, ID3 and ID4 expression was not associated with survival in patients with LUAD. At the protein level, high ID2 significantly predicted an improved survival outcome while high ID1 is associated with shorter survival time. Thus, the results indicate that the ID proteins, particularly ID2, exhibit significant prognostic value in LUAD. More studies are required to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms behind the role of the ID family in the development of LUAD.
Keywords: inhibitor of DNA binding protein family members; lung adenocarcinoma; prognosis.
Copyright: © Lu et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hormonal regulation and differential actions of the helix-loop-helix transcriptional inhibitors of differentiation (Id1, Id2, Id3, and Id4) in Sertoli cells.Endocrinology. 2001 May;142(5):1727-36. doi: 10.1210/endo.142.5.8134. Endocrinology. 2001. PMID: 11316735
-
Prognostic values of the inhibitor of DNA‑binding family members in breast cancer.Oncol Rep. 2018 Oct;40(4):1897-1906. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6589. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30066902 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of inhibitor of differentiation/DNA-binding gene family in lung cancer using bioinformatics methods.Biosci Rep. 2020 Feb 28;40(2):BSR20193075. doi: 10.1042/BSR20193075. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32003423 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitor of differentiation 4 (ID4): From development to cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jan;1855(1):92-103. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2014.12.002. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25512197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of the Expression of Cell Division Cycle-Associated Genes and Its Prognostic Significance in Human Lung Carcinoma: A Review of the Literature Databases.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Feb 12;2020:6412593. doi: 10.1155/2020/6412593. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32104702 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive analysis of ID genes reveals the clinical and prognostic value of ID3 expression in acute myeloid leukemia using bioinformatics identification and experimental validation.BMC Cancer. 2022 Nov 29;22(1):1229. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10352-6. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36443709 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
