Pro-apoptotic activity of novel synthetic isoxazole derivatives exhibiting inhibitory activity against tumor cell growth in vitro
- PMID: 32934719
- PMCID: PMC7471682
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2020.12002
Pro-apoptotic activity of novel synthetic isoxazole derivatives exhibiting inhibitory activity against tumor cell growth in vitro
Abstract
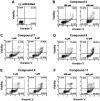
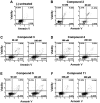
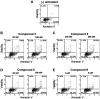
In order to develop potential anticancer agents stimulating apoptosis, novel 3,4-isoxazolediamide and 4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-isoxazolo-[4,5-c]-pyridine derivatives have been synthetized. The original structures of geldanamycin and radicicol, which are known natural heat shock protein (HSP) inhibitors, were deeply modified because both of them exhibit several drawbacks, such as poor solubility, hepatotoxicity, intrinsic chemical instability or deprivation of the in vivo activity. This novel class of synthetic compounds containing the isoxazole nucleus exhibited potent and selective inhibition of HSP90 in previous studies. Biological assays (focusing on in vitro antiproliferative effects and pro-apoptotic activity) in human erythroleukemic K562 cells (as a model system referring to tumor cells grown in suspension), glioblastoma U251-MG and glioblastoma temozolomide (TMZ)-resistant T98G cell lines (two model systems referring to tumor cells grown attached to the flask), were performed. Almost all isoxazole derivatives demonstrated significant antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic activities, showing induction of both early and late apoptosis of K562 cells. Different effects were observed on the glioma U251-MG and T98G cells, depending on the structure of the analogues. Antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic activities in K562 cells were associated with the activation of the erythroid differentiation program. The present study demonstrated that 3,4-isoxazolediamide and 4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-isoxazolo-[4,5-c]-pyridine derivatives should be considered for in vivo studies focusing on the development of anticancer drugs acting, at least partially, via activation of apoptosis.
Keywords: K562 cells; T98G cells; U251-MG cells; apoptosis; cancer; caspases; glioblastoma; heat shock protein inhibitors.
Copyright: © Lampronti et al.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Differential pro-apoptotic effects of synthetic 4-thiazolidinone derivative Les-3288, doxorubicin and temozolomide in human glioma U251 cells.Croat Med J. 2017 Apr 14;58(2):150-159. doi: 10.3325/cmj.2017.58.150. Croat Med J. 2017. PMID: 28409498 Free PMC article.
-
Stereospecific antitumor activity of radicicol oxime derivatives.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2001 Dec;48(6):435-45. doi: 10.1007/s002800100373. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11800023
-
4,5,6,7-Tetrahydro-isoxazolo-[4,5-c]-pyridines as a new class of cytotoxic Hsp90 inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2014 Apr 9;76:53-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.01.056. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Eur J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24565573
-
Geldanamycin, radicicol, and chimeric inhibitors of the Hsp90 N-terminal ATP binding site.Curr Top Med Chem. 2006;6(11):1173-82. doi: 10.2174/156802606777812031. Curr Top Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16842154 Review.
-
Novobiocin Analogs as Potential Anticancer Agents.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2017;17(9):728-733. doi: 10.2174/1389557516666161223155525. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28019639 Review.
Cited by
-
Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of New Multifunctional Benzothiazoles as Photoprotective, Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Agents.Molecules. 2022 Dec 29;28(1):287. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010287. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615480 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Study of Immunological Isoxazole Derivatives as a Potential Support for Melanoma Chemotherapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 10;22(20):10920. doi: 10.3390/ijms222010920. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681580 Free PMC article.
-
New Synthetic Isoxazole Derivatives Acting as Potent Inducers of Fetal Hemoglobin in Erythroid Precursor Cells Isolated from β-Thalassemic Patients.Molecules. 2023 Dec 19;29(1):8. doi: 10.3390/molecules29010008. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38202591 Free PMC article.
-
New Oxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidines as Potential Anticancer Agents: Their Design, Synthesis, and In Vitro Biological Activity Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 2;23(19):11694. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911694. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232997 Free PMC article.
-
Rational Drug Discovery for Isoxazole Based VEGFR2 Inhibition.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2025;22(2):e240524230316. doi: 10.2174/0115701638296906240522072628. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2025. PMID: 38798213
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
