Dose dependence of treatment-related adverse events for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies: a model-based meta-analysis
- PMID: 32934874
- PMCID: PMC7466858
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1748982
Dose dependence of treatment-related adverse events for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies: a model-based meta-analysis
Abstract
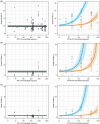
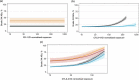
Programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and/or cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) treatments are associated with adverse events (AEs), which may be dependent on ICI dose. Applying a model-based meta-analysis to evaluate safety data from published clinical trials from 2005 to 2018, we analyzed the dose/exposure dependence of ICI treatment-related AE (trAE) and immune-mediated AE (imAE) rates. Unlike with PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy, CTLA-4 inhibitor monotherapy exhibited a dose/exposure dependence on most AE types evaluated. Furthermore, combination therapy with PD-1 inhibitor significantly strengthened the dependence of trAE and imAE rates on CTLA-4 inhibitor dose/exposure.
Keywords: Adverse events; immune checkpoint inhibitor; meta-analysis.
© 2020 The Author(s). Published with license by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
BS, YK, AO, and KP are employees of M&S Decisions LLC, Moscow, Russia, which received funding from AstraZeneca to conduct this research and analysis; LC, GM, SA, RP, GD, GK, and GH are all employees of AstraZeneca.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
