Two Perforators Improve the Extent and Reliability of Paraumbilical Flaps for Upper Limb Reconstruction
- PMID: 32934933
- PMCID: PMC7482532
- DOI: 10.29252/wjps.9.2.206
Two Perforators Improve the Extent and Reliability of Paraumbilical Flaps for Upper Limb Reconstruction
Abstract
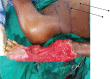
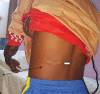
Background: Complex defects of the forearm and arm are best reconstructed with free flaps. Free flaps are however not universally available. They require long operative time and may be contraindicated in patients with extensive injuries due to a lack of good recipient vessels. The alternatives to free flaps are distant flaps such as groin flaps, random abdominal flaps, thoracoepigastric flaps and paraumbilical perforator flaps. These are axial flaps that are limited by the angiosomes supplied by a given perforator or blood vessel. To improve the extent and reliabilities of the paraumbilical flaps, we incorporated two perforators in the flap.
Methods: A total of 17 patients with extensive forearm defects were managed by two vessel paraumbilical perforator flaps between January 2013 and December 2018. The perforators were identified by a hand-held Doppler and the flap was fashioned with the perforators at the base.
Results: The mean length of the flap raised was 19.5 cm and width was 8.3 cm. The median age was 39 years. All the flaps were successful with no incidence of flap necrosis and no dehiscence.
Conclusion: Two vessel perforator flaps improved the reliability of the paraumbilical perforator flap, allowing for a bigger flap to be harvested and thus ensuring a cover of larger defects. The flaps were easy to raise and were easily tolerated by the patients.
Keywords: Forearm; Limb; Paraumbilical flap; Perforator; Reconstruction.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Reconstruction of extensive upper extremity defects using pre-expanded oblique perforator-based paraumbilical flaps.Burns. 2012 Sep;38(6):917-23. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2012.01.002. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Burns. 2012. PMID: 22360960
-
Lateralising paraumbilical medial row perforators: dangers and pitfalls in DIEP FLAP planning: a systematic review of 1116 DIEP flaps.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014 Mar;67(3):383-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2013.12.017. Epub 2013 Dec 27. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014. PMID: 24388599
-
Perforator Peroneal Artery Flap for Tongue Reconstruction.J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2017 Mar;16(1):123-126. doi: 10.1007/s12663-016-0933-3. Epub 2016 Jul 11. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2017. PMID: 28286397 Free PMC article.
-
"Wing flaps": perforator-based pedicled paraumbilical flaps for skin defects in hand and forearm.Ann Plast Surg. 2007 Nov;59(5):495-500. doi: 10.1097/01.sap.0000258936.51029.09. Ann Plast Surg. 2007. PMID: 17992141
-
Tips on Raising Reliable Local Perforator Flaps.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021 Jul 28;9(7):e3673. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000003673. eCollection 2021 Jul. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021. PMID: 34422514 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Application strategy and clinical effects of paraumbilical perforator flap with inferior epigastric vessels in repairing destructive wounds].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2021 Jul 20;37(7):606-613. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20210310-00082. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34192852 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Munot R, Devale M, Munoli A. A Study on the use of Abdominal Flaps to Reconstruct Upper Limb Defects. Journal of Medical Science and Clinical Research . 2016:49–54.
-
- Chen HC, Tang YB, Mardini S, Tsai BW. Reconstruction of the hand and upper limb with free flaps based on musculocutaneous perforators. Microsurgery. 2004;24:270–80. - PubMed
-
- Gutwein LG, Merrell GA, Knox KR. Paraumbilical perforator flap for soft tissue reconstruction of the forearm. J Hand Surg Am. 2015;40:586–92. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
