From microbiota toward gastro-enteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: Are we on the highway to hell?
- PMID: 32935263
- PMCID: PMC8346435
- DOI: 10.1007/s11154-020-09589-y
From microbiota toward gastro-enteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: Are we on the highway to hell?
Abstract
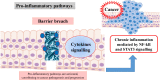
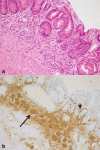
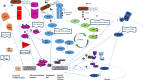
Gut microbiota is represented by different microorganisms that colonize the intestinal tract, mostly the large intestine, such as bacteria, fungi, archaea and viruses. The gut microbial balance has a key role in several functions. It modulates the host's metabolism, maintains the gut barrier integrity, participates in the xenobiotics and drug metabolism, and acts as protection against gastro-intestinal pathogens through the host's immune system modulation. The impaired gut microbiota, called dysbiosis, may be the result of an imbalance in this equilibrium and is linked with different diseases, including cancer. While most of the studies have focused on the association between microbiota and gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas, very little is known about gastroenteropancreatic (GEP) neuroendocrine neoplasms (NENs). In this review, we provide an overview concerning the complex interplay between gut microbiota and GEP NENs, focusing on the potential role in tumorigenesis and progression in these tumors.
Keywords: Cytokines; Inflammation; Microbiota; Neuroendocrine tumors; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2020. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A. Colao has received consultant fees from Novartis and Ipsen. A. Faggiano has received consultant fee from Triple AAA and Ipsen. G. Vitale has received consultant fees from Novartis.
Figures


References
-
- Muscogiuri G, Balercia G, Barrea L, Cignarelli A, Giorgino F, Holst JJ, et al. Gut: a key player in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes? Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2018;24:1294–309. - PubMed
-
- Barrea L, Muscogiuri G, Annunziata G, Laudisio D, Pugliese G, Salzano C, et al. From gut microbiota dysfunction to obesity: could short-chain fatty acids stop this dangerous course? Hormones (Athens). 2019;18:245–50. - PubMed

