IL-37: An anti-inflammatory cytokine with antitumor functions
- PMID: 32935478
- PMCID: PMC7941439
- DOI: 10.1002/cnr2.1151
IL-37: An anti-inflammatory cytokine with antitumor functions
Abstract
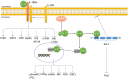
Background: IL-37 is a newly identified IL-1 family cytokine. Unlike other members in IL-1 family, IL-37 has been demonstrated to be an anti-inflammatory cytokine in many inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. IL-37 is regarded as a dual-function cytokine as both the extracellular and intracellular IL-37 are biologically functional. Extracellular IL-37 can bind to IL-18Rα and IL-1R8 to form a triple complex, regulating the downstream STAT3 and PTEN signaling. Intracellular IL-37 can interact with Smad3, translocate into nucleus, and regulate downstream target gene expressions. Recently, the role of IL-37 in tumor development has been extensively studied.
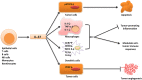
Recent findings: IL-37 has been found to play an antitumor role in various types of tumors, such as non-small cell lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and renal cell carcinoma. Many mechanism studies have been carried out to elaborate the possible effects of IL-37 on tumor growth, immune responses, and tumor angiogenesis. More importantly, the function of IL-37 may be dependent on its concentration and receptor expression. It can form dimers at high concentrations to be inactivated, thus inhibiting its anti-inflammatory function. We focused on the role of IL-37 in various tumor types and provided the hypothesis regarding the underlying mechanisms.
Conclusion: IL-37 may affect tumor development through multiple mechanisms: (1) IL-37 directly influences tumor cell viability; (2) IL-37 regulates the immune response to promote the antitumor immunity; and (3) IL-37 suppresses tumor angiogenesis in the tumor microenvironment. Future studies are warranted to further investigate the mechanisms of these multifaceted functions of IL-37 in animal models and cancer patients.
Keywords: IL‐37; angiogenesis; antitumor immune response; inflammation.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Busfield SJ, Comrack CA, Yu G, et al. Identification and gene organization of three novel members of the IL‐1 family on human chromosome 2. Genomics. 2000;66(2):213‐216. - PubMed
-
- Kumar S, McDonnell PC, Lehr R, et al. Identification and initial characterization of four novel members of the interleukin‐1 family. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(14):10308‐10314. - PubMed
-
- Pan G, Risser P, Mao W, et al. IL‐1H, an interleukin 1‐related protein that binds IL‐18 receptor/IL‐1Rrp. Cytokine. 2001;13(1):1‐7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

