Evaluation and Management of Difficult-to-Treat and Severe Asthma: An Expert Opinion From the Korean Academy of Asthma, Allergy and Clinical Immunology, the Working Group on Severe Asthma
- PMID: 32935486
- PMCID: PMC7492516
- DOI: 10.4168/aair.2020.12.6.910
Evaluation and Management of Difficult-to-Treat and Severe Asthma: An Expert Opinion From the Korean Academy of Asthma, Allergy and Clinical Immunology, the Working Group on Severe Asthma
Abstract
Severe asthma (SA) presents in about 3%-5% of adult asthmatics and is responsible for over 60% of asthma-related medical expenses, posing a heavy socioeconomic burden. However, to date, a precise definition of or clear diagnostic criteria for SA have not been established, and therefore, it has been challenging for clinicians to diagnose and treat this disease. Currently, novel biologics targeting several molecules, such as immunoglobulin E, interleukin (IL)5, and IL4/IL13, have emerged, and many new drugs are under development. These have brought a paradigm shift in understanding the mechanism of SA and have also provided new treatment options. However, we need to agree on a precise definition of and its diagnostic criteria for SA. Additionally, it is necessary to explain the diagnostic criteria and to summarize current standard and additional treatment options. This review is an experts' opinion on SA from the Korean Academy of Asthma, Allergy, and Clinical Immunology, the Working Group on Severe Asthma, and aims to provide a definition of and diagnostic criteria for SA, and propose future direction for SA diagnosis and management in Korea.
Keywords: IL4; IgE; Severe asthma; biologics; diagnosis; eosinophil; expert opinion; treatment, IL5.
Copyright © 2020 The Korean Academy of Asthma, Allergy and Clinical Immunology · The Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no financial or other issues that might lead to conflict of interest.
Figures

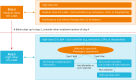
References
-
- Chung KF, Wenzel SE, Brozek JL, Bush A, Castro M, Sterk PJ, et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma. Eur Respir J. 2014;43:343–373. - PubMed
-
- Holguin F, Cardet JC, Chung KF, Diver S, Ferreira DS, Fitzpatrick A, et al. Management of severe asthma: a European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society guideline. Eur Respir J. 2020;55:1900588. - PubMed
-
- Proceedings of the ATS workshop on refractory asthma: current understanding, recommendations, and unanswered questions. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;162:2341–2351. - PubMed
-
- Bousquet J, Mantzouranis E, Cruz AA, Aït-Khaled N, Baena-Cagnani CE, Bleecker ER, et al. Uniform definition of asthma severity, control, and exacerbations: document presented for the World Health Organization Consultation on Severe Asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;126:926–938. - PubMed

