Isolable Silicon-Based Polycations with Lewis Superacidity
- PMID: 32935903
- PMCID: PMC7756528
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202011696
Isolable Silicon-Based Polycations with Lewis Superacidity
Abstract
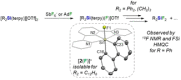
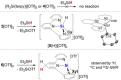
Molecular silicon polycations of the types R2 Si2+ and RSi3+ (R=H, organic groups) are elusive Lewis superacids and currently unknown in the condensed phase. Here, we report the synthesis of a series of isolable terpyridine-stabilized R2 Si2+ and RSi3+ complexes, [R2 Si(terpy)]2+ (R=Ph 12+ ; R2 =C12 H8 22+ , (CH2 )3 32+ ) and [RSi(terpy)]3+ (R=Ph 43+ , cyclohexyl 53+ , m-xylyl 63+ ), in form of their triflate salts. The stabilization of the latter is achieved through higher coordination and to the expense of reduced fluoride-ion affinities, but a significant level of Lewis superacidity is nonetheless retained as verified by theory and experiment. The complexes activate C(sp3 )-F bonds, as showcased by stoichiometric fluoride abstraction from 1-fluoroadamantane (AdF) and the catalytic hydrodefluorination of AdF. The formation of the crystalline adducts [2(F)]+ and [5(H)]2+ documents in particular the high reactivity towards fluoride and hydride donors.
Keywords: Coordination compounds; Hydride transfer; Hydrodefluorination; Main group elements; Silanes.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- None
-
- Sereda O., Tabassum S., Wilhelm R. in Topics in Current Chemistry (Ed.: List B.), Springer, Heidelberg, 2009, pp. 349–393; - PubMed
-
- Weicker S. A., Stephan D. W., Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 88, 1003–1016;
-
- Davydova E. I., Sevastianova T. N., Timoshkin A. Y., Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 297–298, 91–126;
-
- Stephan D. W., Erker G., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 46–76; - PubMed
- Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 50–81.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

