Artificial Intelligence for the Prediction of Helicobacter Pylori Infection in Endoscopic Images: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Of Diagnostic Test Accuracy
- PMID: 32936088
- PMCID: PMC7527948
- DOI: 10.2196/21983
Artificial Intelligence for the Prediction of Helicobacter Pylori Infection in Endoscopic Images: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Of Diagnostic Test Accuracy
Abstract
Background: Helicobacter pylori plays a central role in the development of gastric cancer, and prediction of H pylori infection by visual inspection of the gastric mucosa is an important function of endoscopy. However, there are currently no established methods of optical diagnosis of H pylori infection using endoscopic images. Definitive diagnosis requires endoscopic biopsy. Artificial intelligence (AI) has been increasingly adopted in clinical practice, especially for image recognition and classification.
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic test accuracy of AI for the prediction of H pylori infection using endoscopic images.
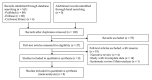
Methods: Two independent evaluators searched core databases. The inclusion criteria included studies with endoscopic images of H pylori infection and with application of AI for the prediction of H pylori infection presenting diagnostic performance. Systematic review and diagnostic test accuracy meta-analysis were performed.
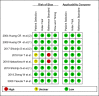
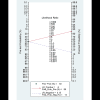
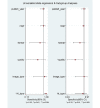
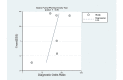
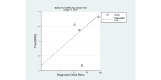
Results: Ultimately, 8 studies were identified. Pooled sensitivity, specificity, diagnostic odds ratio, and area under the curve of AI for the prediction of H pylori infection were 0.87 (95% CI 0.72-0.94), 0.86 (95% CI 0.77-0.92), 40 (95% CI 15-112), and 0.92 (95% CI 0.90-0.94), respectively, in the 1719 patients (385 patients with H pylori infection vs 1334 controls). Meta-regression showed methodological quality and included the number of patients in each study for the purpose of heterogeneity. There was no evidence of publication bias. The accuracy of the AI algorithm reached 82% for discrimination between noninfected images and posteradication images.
Conclusions: An AI algorithm is a reliable tool for endoscopic diagnosis of H pylori infection. The limitations of lacking external validation performance and being conducted only in Asia should be overcome.
Trial registration: PROSPERO CRD42020175957; https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=175957.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; artificial intelligence; convolutional neural network; deep learning; endoscopy; machine learning.
©Chang Seok Bang, Jae Jun Lee, Gwang Ho Baik. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (http://www.jmir.org), 16.09.2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Hooi JKY, Lai WY, Ng WK, Suen MMY, Underwood FE, Tanyingoh D, Malfertheiner P, Graham DY, Wong VWS, Wu JCY, Chan FKL, Sung JJY, Kaplan GG, Ng SC. Global prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection: systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2017 Aug;153(2):420–429. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.04.022. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0016-5085(17)35531-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Correa P. A human model of gastric carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1988 Jul 01;48(13):3554–3560. http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=3288329 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

