Remote Optimization of Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy in Patients With Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction
- PMID: 32936209
- PMCID: PMC7495335
- DOI: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.3757
Remote Optimization of Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy in Patients With Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction
Erratum in
-
Error in Supplement.JAMA Cardiol. 2021 Apr 1;6(4):485. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2021.0091. JAMA Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33625470 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: Optimal treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) is scripted by treatment guidelines, but many eligible patients do not receive guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) in clinical practice.
Objective: To determine whether a remote, algorithm-driven, navigator-administered medication optimization program could enhance implementation of GDMT in HFrEF.
Design, setting, and participants: In this case-control study, a population-based sample of patients with HFrEF was offered participation in a quality improvement program directed at GDMT optimization. Treating clinicians in a tertiary academic medical center who were caring for patients with heart failure and an ejection fraction of 40% or less (identified through an electronic health record-based search) were approached for permission to adjust medical therapy according to a sequential titration algorithm modeled on the current American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association heart failure guidelines. Navigators contacted participants by telephone to direct medication adjustment and conduct longitudinal surveillance of laboratory tests, blood pressure, and symptoms under supervision of a pharmacist, nurse practitioner, and heart failure cardiologist. Patients and clinicians declining to participate served as a control group.
Exposures: Navigator-led remote optimization of GDMT compared with usual care.
Main outcomes and measures: Proportion of patients receiving GDMT in the intervention and control groups at 3 months.
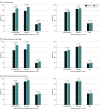
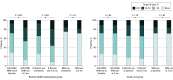
Results: Of 1028 eligible patients (mean [SD] values: age, 68 [14] years; ejection fraction, 32% [8%]; and systolic blood pressure, 122 [18] mm Hg; 305 women (30.0%); 892 individuals [86.8%] in New York Heart Association class I and II), 197 (19.2%) participated in the medication optimization program, and 831 (80.8%) continued with usual care as directed by their treating clinicians (585 [56.9%] general cardiologists; 443 [43.1%] heart failure specialists). At 3 months, patients participating in the remote intervention experienced significant increases from baseline in use of renin-angiotensin system antagonists (138 [70.1%] to 170 [86.3%]; P < .001) and β-blockers (152 [77.2%] to 181 [91.9%]; P < .001) but not mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (51 [25.9%] to 60 [30.5%]; P = .14). Doses for each category of GDMT also increased from baseline in the intervention group. Among the usual-care group, there were no changes from baseline in the proportion of patients receiving GDMT or the dose of GDMT in any category.
Conclusions and relevance: Remote titration of GDMT by navigators using encoded algorithms may represent an efficient, population-level strategy for rapidly closing the gap between guidelines and clinical practice in patients with HFrEF.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
An Excellent Model to Increase Adherence to Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy-With Far-reaching Implications.JAMA Cardiol. 2021 Jun 1;6(6):726. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2021.0321. JAMA Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33787819 No abstract available.
-
An Excellent Model to Increase Adherence to Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy-With Far-reaching Implications-Reply.JAMA Cardiol. 2021 Jun 1;6(6):726-727. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2021.0327. JAMA Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33787827 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Rationale and design of a navigator-driven remote optimization of guideline-directed medical therapy in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.Clin Cardiol. 2020 Jan;43(1):4-13. doi: 10.1002/clc.23291. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Clin Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 31725920 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a guideline directed medical therapy titration program in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2018 Nov 8;22:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2018.10.003. eCollection 2019 Mar. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2018. PMID: 30480083 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual optimization of guideline-directed medical therapy in hospitalized patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: the IMPLEMENT-HF pilot study.Eur J Heart Fail. 2021 Jul;23(7):1191-1201. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2163. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Eur J Heart Fail. 2021. PMID: 33768599
-
Evaluation of the Usage and Dosing of Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy for Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction Patients in Clinical Practice.J Pharm Pract. 2022 Oct;35(5):747-751. doi: 10.1177/08971900211004840. Epub 2021 Apr 5. J Pharm Pract. 2022. PMID: 33813934 Review.
-
Interventions for Optimization of Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy: A Systematic Review.JAMA Cardiol. 2024 Apr 1;9(4):397-404. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2023.5627. JAMA Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38381449
Cited by
-
Heart Failure Management through Telehealth: Expanding Care and Connecting Hearts.J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 28;13(9):2592. doi: 10.3390/jcm13092592. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38731120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Electronically Delivered Patient-Activation Tool for Intensification of Medications for Chronic Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction: The EPIC-HF Trial.Circulation. 2021 Feb 2;143(5):427-437. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.051863. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Circulation. 2021. PMID: 33201741 Free PMC article.
-
Digital solutions to optimize guideline-directed medical therapy prescription rates in patients with heart failure: a clinical consensus statement from the ESC Working Group on e-Cardiology, the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, the Association of Cardiovascular Nursing & Allied Professions of the European Society of Cardiology, the ESC Digital Health Committee, the ESC Council of Cardio-Oncology, and the ESC Patient Forum.Eur Heart J Digit Health. 2024 Aug 30;5(6):670-682. doi: 10.1093/ehjdh/ztae064. eCollection 2024 Nov. Eur Heart J Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 39563907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early and rapid initiation of quadruple therapy for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: A real-world experience.Clin Med (Lond). 2025 Mar;25(2):100296. doi: 10.1016/j.clinme.2025.100296. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Clin Med (Lond). 2025. PMID: 39986470 Free PMC article.
-
Multiregional Implementation Initiative's Impact on Guideline-Based Performance Measures for Patients Hospitalized With Heart Failure: IMPLEMENT-HF.Circ Heart Fail. 2025 May;18(5):e012547. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.124.012547. Epub 2025 Mar 21. Circ Heart Fail. 2025. PMID: 40115978 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

