A polyclonal antibody against a recombinantly expressed Triticum aestivum RHT-D1A protein
- PMID: 32936364
- PMCID: PMC7494718
- DOI: 10.1186/s43141-020-00072-4
A polyclonal antibody against a recombinantly expressed Triticum aestivum RHT-D1A protein
Abstract
Background: Reduced height-1 dwarfing alleles affect DELLA proteins belonging to a family of putative transcriptional regulators that modulate plant growth and development. The Arabidopsis thaliana genome encodes five DELLA proteins, whereas monocot plants, such as rice, barley, and wheat, each have a single DELLA protein. In wheat, wild-type Rht-B1a and Rht-D1a genes encode DELLA proteins and have many alleles that contain lesions. Among them, Rht-B1b and Rht-D1b are the most common mutant dwarfing alleles, which have played a key part in the creation of high-yielding wheat varieties. Despite their fundamental roles in plant biology, until now, DELLA proteins in wheat have been mainly researched regarding the phenotypic effect of defective Rht mutants on yield-related traits, without studies on the underlying mechanisms. The RHT-1 protein has yet to be detected in wheat tissues, owing to a lack of appropriate molecular tools for characterization of RHT function and protein interactions in signal transduction. This study is focused on the production of a polyclonal antibody to the wheat RHT-D1A protein.
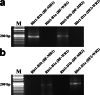
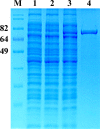
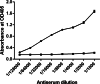
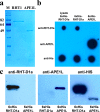
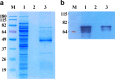
Results: To generate the anti-RHT-D1A antibody, we expressed and purified soluble 6xHis-tagged RHT-D1A. The purified recombinant RHT-D1A was injected into New Zealand white rabbits to generate polyclonal antiserum. The polyclonal anti-RHT-D1A antibody was purified by ammonium sulfate precipitation, followed by affinity chromatography on protein A-agarose beads. The purified polyclonal antibody was demonstrated to be effective in immunoblotting, western blot hybridization, and immunoprecipitation. In wheat seedling extracts, the polyclonal antibody recognized a protein with a molecular mass close to the predicted molecular weight of the endogenous RHT-D1A protein. We also demonstrated that RHT-D1A disappears in response to exogenous and endogenous gibberellic acid.
Conclusion: The purified polyclonal antibody raised against the recombinant RHT-D1A protein is sufficiently specific and sensitive and could be a useful tool for future insights into upstream and downstream components of DELLA-regulatory mechanisms in wheat plants.
Keywords: DELLA; Norin 10; Polyclonal antibody; RHT-D1A; Saratovskaya 29; Triticum aestivum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Guedira M, Brown-Guedira G, Van Sanford D, Sneller C, Souza E, Marshall D. Distribution of Rht genes in modern and historic winter wheat cultivars from the Eastern and Central USA. Crop Sci. 2010;50:1811–1822. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2009.10.0626. - DOI
-
- Flintham JE, Borner A, Worland AJ, Gale MD. Optimizing wheat grain yield: effects of Rht (gibberellin-insensitive) dwarfing genes. J Agr Sci. 1997;128:11–25. doi: 10.1017/S0021859696003942. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
