Individual dynamics of delta-beta coupling: using a multilevel framework to examine inter- and intraindividual differences in relation to social anxiety and behavioral inhibition
- PMID: 32936944
- PMCID: PMC7960561
- DOI: 10.1111/jcpp.13319
Individual dynamics of delta-beta coupling: using a multilevel framework to examine inter- and intraindividual differences in relation to social anxiety and behavioral inhibition
Abstract
Background: Variation in EEG-derived delta-beta coupling has recently emerged as a potential neural marker of emotion regulation, providing a novel and noninvasive method for assessing a risk factor for anxiety. However, our understanding of delta-beta coupling has been limited to group-level comparisons, which provide limited information about an individual's neural dynamics.
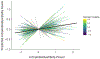
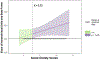
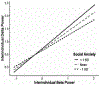
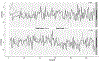
Methods: The present study used multilevel modeling to map second-by-second coupling patterns between delta and beta power. Specifically, we examined how inter- and intraindividual delta-beta coupling patterns changed as a function of social anxiety symptoms and temperamental behavioral inhibition (BI).
Results: We found that stronger inter- and intraindividual delta-beta coupling were both associated with social anxiety. In contrast, the high-BI group showed weaker coupling relative to the non-BI group, a pattern that did not emerge when analyzing continuous scores of BI.
Conclusions: In characterizing inter- and intraindividual coupling across the sample, we illustrate the utility of examining neural processes across levels of analysis in relation to psychopathology to create multilevel assessments of functioning and risk.
Keywords: Delta-beta coupling; behavioral inhibition; intraindividual variability; social anxiety.
© 2020 Association for Child and Adolescent Mental Health.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Disentangling the role of different resting-state neural markers of adolescent behavioral inhibition and social anxiety.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2025 Jun;73:101560. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2025.101560. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40306167 Free PMC article.
-
Dyadic behavioral synchrony between behaviorally inhibited and non-inhibited peers is associated with concordance in EEG frontal Alpha asymmetry and Delta-Beta coupling.Biol Psychol. 2021 Feb;159:108018. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2021.108018. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Biol Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33450325 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions among stress, behavioral inhibition, and delta-beta coupling predict adolescent anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic.Dev Psychobiol. 2024 Apr;66(3):e22485. doi: 10.1002/dev.22485. Dev Psychobiol. 2024. PMID: 38483054 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral inhibition: a neurobiological perspective.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2006 Aug;8(4):270-8. doi: 10.1007/s11920-006-0062-7. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2006. PMID: 16879790 Review.
-
Linear and Nonlinear EEG-Based Functional Networks in Anxiety Disorders.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1191:35-59. doi: 10.1007/978-981-32-9705-0_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32002921 Review.
Cited by
-
From Infancy to Childhood: A Comprehensive Review of Event- and Task-Related Brain Oscillations.Brain Sci. 2024 Aug 20;14(8):837. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14080837. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39199528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disentangling the role of different resting-state neural markers of adolescent behavioral inhibition and social anxiety.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2025 Jun;73:101560. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2025.101560. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40306167 Free PMC article.
-
Deriving within-person estimates of delta-beta coupling: A novel measure for identifying individual differences in emotion and neural function in childhood.Dev Psychobiol. 2021 Sep;63(6):e22172. doi: 10.1002/dev.22172. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Dev Psychobiol. 2021. PMID: 34343349 Free PMC article.
-
Dyadic behavioral synchrony between behaviorally inhibited and non-inhibited peers is associated with concordance in EEG frontal Alpha asymmetry and Delta-Beta coupling.Biol Psychol. 2021 Feb;159:108018. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2021.108018. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Biol Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33450325 Free PMC article.
-
The wobbly bits of development: Variability, fluctuations, and synchrony as temporal markers linking temperament and psychopathology.Curr Dir Psychol Sci. 2025 Jun;34(3):171-178. doi: 10.1177/09637214241311919. Epub 2025 Mar 30. Curr Dir Psychol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40771435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2015). Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67(1), 1–48. 10.18637/jss.v067.i01 - DOI
-
- Bishop G, Spence SH, & McDonald C (2003). Can parents and teachers provide a reliable and valid report of behavioral inhibition? Child Development, 74, 1899–1917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

