Efficacy and safety of co-administered telmisartan/amlodipine and rosuvastatin in subjects with hypertension and dyslipidemia
- PMID: 32937023
- PMCID: PMC7692919
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.13893
Efficacy and safety of co-administered telmisartan/amlodipine and rosuvastatin in subjects with hypertension and dyslipidemia
Abstract
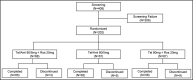
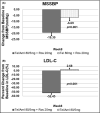
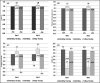
Single risk factors, such as hypertension and dyslipidemia, can combine to exacerbate the development and severity of cardiovascular disease. Treatment goals may be more effectively achieved if multiple disease factors are targeted with combination treatment. We enrolled 202 patients who were randomly divided into the following three groups: telmisartan/amlodipine 80/5 mg + rosuvastatin 20 mg, telmisartan 80 mg + rosuvastatin 20 mg, and telmisartan/amlodipine 80/5 mg. The primary efficacy variables were changes from baseline in mean sitting systolic blood pressure (MSSBP) between telmisartan/amlodipine 80/5 mg + rosuvastatin 20 mg and telmisartan 80 mg + rosuvastatin 20 mg at 8 weeks, and the percent changes from baseline in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol between telmisartan/amlodipine 80/5 mg + rosuvastatin 20 mg and telmisartan/amlodipine 80/5 mg at 8 weeks. The secondary efficacy variables were changes in MSSBP, mean sitting diastolic blood pressure (MSDBP), LDL cholesterol and other lipid levels at 4 weeks and 8 weeks, as well as observed adverse events during follow-up. There were no significant differences between the three groups in demographic characteristics and no significant difference among the three groups in terms of baseline characteristics for the validity evaluation variables. The mean overall treatment compliance in the three groups was, respectively, 98.42%, 96.68%, and 98.12%, indicating strong compliance for all patients. The Least-Square (LS) mean (SE) for changes in MSSBP in the two (telmisartan/amlodipine 80/5 mg + rosuvastatin 20 mg and telmisartan 80 mg + rosuvastatin 20 mg) groups were -19.3 (2.68) mm Hg and -6.69 (2.76) mm Hg. The difference between the two groups was significant (-12.60 (2.77) mm Hg, 95% CI -18.06 to -7.14, P < .0001). The LS Mean for the percent changes from baseline in LDL cholesterol in the two (telmisartan/amlodipine 80/5 mg + rosuvastatin 20 mg and telmisartan/amlodipine 80/5 mg) groups were -52.45 (3.23) % and 2.68 (3.15) %. The difference between the two groups was significant (-55.13 (3.20) %, 95% CI -61.45 to -48.81, P < .0001). There were no adverse events leading to discontinuation or death. Combined administration of telmisartan/amlodipine 80/5 mg and rosuvastatin 20 mg for the treatment of hypertensive patients with dyslipidemia significantly reduces blood pressure and improves lipid control. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03067688.
Keywords: amlodipine; dyslipidemia; hypertension; rosuvastatin; telmisartan.
© 2020 The Authors. The Journal of Clinical Hypertension published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Moo‐Yong Rhee has received lecture honoraria from Pfizer Inc, LG Life Sciences Ltd, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG., Hanmi Pharm. Co. Ltd., Yuhan Co. Ltd., and Boryung Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.; fees for consulting from Hanmi Pharm. Co. Ltd. and Shin Poong Pharma. Co. Ltd.; and research grants from Boryung Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. and Dong‐A Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. Hana Lee and Yoonhwa Cho are salaried employees of Yuhan Corporation. The other authors have indicated that they have no other conflicts of interest regarding the content of this article. The sponsor, Yuhan Corporation supported the supply of the study drug, laboratory tests, data collection, and data analysis. The sponsor had no role in data interpretation, the writing of the original draft of manuscript, or the decision to submit the article for publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and Safety of Triple Therapy With Telmisartan, Amlodipine, and Rosuvastatin in Patients With Dyslipidemia and Hypertension: The Jeil Telmisartan, Amlodipine, and Rosuvastatin Randomized Clinical Trial.Clin Ther. 2019 Feb;41(2):233-248.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2018.12.008. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Clin Ther. 2019. PMID: 30665829 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Fixed-dose Combination Therapy With Telmisartan and Rosuvastatin in Korean Patients With Hypertension and Dyslipidemia: TELSTA-YU (TELmisartan-rosuvaSTAtin from YUhan), a Multicenter, Randomized, 4-arm, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Phase III Study.Clin Ther. 2018 May;40(5):676-691.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2018.03.010. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Clin Ther. 2018. PMID: 29673890 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Tolerability of Telmisartan/Amlodipine and Rosuvastatin Coadministration in Hypertensive Patients with Hyperlipidemia: A Phase III, Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind Study.Clin Ther. 2019 Apr;41(4):728-741. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.02.013. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Clin Ther. 2019. PMID: 30904178 Clinical Trial.
-
Triple Therapy with Telmisartan, Amlodipine, and Rosuvastatin (TAR) Versus Telmisartan/Amlodipine (TA) and Telmisartan/Rosuvastatin (TR) Combinations in Hypertension and Dyslipidemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2025 Jan;32(1):49-60. doi: 10.1007/s40292-024-00689-3. Epub 2024 Nov 19. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2025. PMID: 39557773
-
Review: a single-pill combination of telmisartan plus amlodipine for the treatment of hypertension.Postgrad Med. 2011 Nov;123(6):58-65. doi: 10.3810/pgm.2011.11.2495. Postgrad Med. 2011. PMID: 22104454 Review.
Cited by
-
Statin's role on blood pressure levels: Meta-analysis based on randomized controlled trials.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2023 Mar;25(3):238-250. doi: 10.1111/jch.14645. Epub 2023 Feb 17. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2023. PMID: 36799888 Free PMC article.
-
Statins As Anti-Hypertensive Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Apr 8;16(4):e57825. doi: 10.7759/cureus.57825. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38721173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telmisartan combined with calcitriol enhances therapeutic efficacy for diabetic nephropathy while inhibiting inflammation and renal interstitial fibrosis.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Nov 15;15(11):6543-6550. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 38074815 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Triple Therapy of Telmisartan/Amlodipine/Rosuvastatin in Patients with Dyslipidemia and Hypertension: A Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial.Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2024 Feb 1;100:100735. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100735. eCollection 2024. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2024. PMID: 38380420 Free PMC article.
-
Safety of combined drug use in patients with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases: an analysis based on the spontaneous reporting database of adverse drug reactions in Hubei Province.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 8;15:1451713. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1451713. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39845792 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnson ML, Pietz K, Battleman DS, et al. Prevalence of comorbid hypertension and dyslipidemia and associated cardiovascular disease. Heart Dis. 2004;2:3. - PubMed
-
- Jackson R, Lawes CMM, Bennett DA, et al. Treatment with drugs to lower blood pressure and blood cholesterol based on an individual's absolute cardiovascular risk. Lancet. 2005;365(9457):434‐441. - PubMed
-
- Dezii CM. A retrospective study of persistence with single‐pill combination therapy vs. concurrent two‐pill therapy in patients with hypertension. Manag Care (Langhorne, PA). 2000;9(9 Suppl):2‐6. - PubMed
-
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;71:e127ee248. - PubMed
-
- Wald DS, Law M, Morris JK, et al. Combination therapy versus monotherapy in reducing blood pressure: meta‐analysis on 11,000 participants from 42 trials. Am J Med. 2009;122(3):290‐300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

