DELTEX2 C-terminal domain recognizes and recruits ADP-ribosylated proteins for ubiquitination
- PMID: 32937373
- PMCID: PMC7442474
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abc0629
DELTEX2 C-terminal domain recognizes and recruits ADP-ribosylated proteins for ubiquitination
Abstract
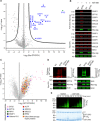
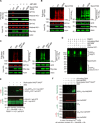
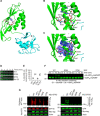
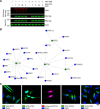
Cross-talk between ubiquitination and ADP-ribosylation regulates spatiotemporal recruitment of key players in many signaling pathways. The DELTEX family ubiquitin ligases (DTX1 to DTX4 and DTX3L) are characterized by a RING domain followed by a C-terminal domain (DTC) of hitherto unknown function. Here, we use two label-free mass spectrometry techniques to investigate the interactome and ubiquitinated substrates of human DTX2 and identify a large proportion of proteins associated with the DNA damage repair pathway. We show that DTX2-catalyzed ubiquitination of these interacting proteins requires PARP1/2-mediated ADP-ribosylation and depends on the DTC domain. Using a combination of structural, biochemical, and cell-based techniques, we show that the DTX2 DTC domain harbors an ADP-ribose-binding pocket and recruits poly-ADP-ribose (PAR)-modified proteins for ubiquitination. This PAR-binding property of DTC domain is conserved across the DELTEX family E3s. These findings uncover a new ADP-ribose-binding domain that facilitates PAR-dependent ubiquitination.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures

References
-
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A., The ubiquitin system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 425–479 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Komander D., Rape M., The ubiquitin code. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 81, 203–229 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Deshaies R. J., Joazeiro C. A., RING domain E3 ubiquitin ligases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 78, 399–434 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Dye B. T., Schulman B. A., Structural mechanisms underlying posttranslational modification by ubiquitin-like proteins. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 36, 131–150 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Kishi N., Tang Z., Maeda Y., Hirai A., Mo R., Ito M., Suzuki S., Nakao K., Kinoshita T., Kadesch T., Hui C.-c., Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Okano H., Matsuno K., Murine homologs of deltex define a novel gene family involved in vertebrate Notch signaling and neurogenesis. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 19, 21–35 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

