Identification of human CD4+ T cell populations with distinct antitumor activity
- PMID: 32937437
- PMCID: PMC7458458
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aba7443
Identification of human CD4+ T cell populations with distinct antitumor activity
Abstract
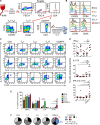
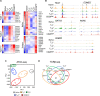
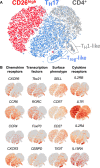
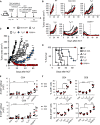
How naturally arising human CD4+ T helper subsets affect cancer immunotherapy is unclear. We reported that human CD4+CD26high T cells elicit potent immunity against solid tumors. As CD26high T cells are often categorized as TH17 cells for their IL-17 production and high CD26 expression, we posited these populations would have similar molecular properties. Here, we reveal that CD26high T cells are epigenetically and transcriptionally distinct from TH17 cells. Of clinical importance, CD26high and TH17 cells engineered with a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) regressed large human tumors to a greater extent than enriched TH1 or TH2 cells. Only human CD26high T cells mediated curative responses, even when redirected with a suboptimal CAR and without aid by CD8+ CAR T cells. CD26high T cells cosecreted effector cytokines, produced cytotoxic molecules, and persisted long term. Collectively, our work underscores the promise of CD4+ T cell populations to improve durability of solid tumor therapies.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures
References
-
- Ohnuma K., Dang N. H., Morimoto C., Revisiting an old acquaintance: CD26 and its molecular mechanisms in T cell function. Trends Immunol. 29, 295–301 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Fleischer B., CD26: A surface protease involved in T-cell activation. Immunol. Today 15, 180–184 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Dang N. H., Torimoto Y., Sugita K., Daley J. F., Schow P., Prado C., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C., Cell surface modulation of CD26 by anti-1F7 monoclonal antibody. Analysis of surface expression and human T cell activation. J. Immunol. 145, 3963–3971 (1990). - PubMed
-
- Paulissen S. M. J., van Hamburg J. P., Dankers W., Lubberts E., The role and modulation of CCR6+ Th17 cell populations in rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine 74, 43–53 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

