Flavonoids as Phytoestrogenic Components of Hops and Beer
- PMID: 32937790
- PMCID: PMC7570471
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25184201
Flavonoids as Phytoestrogenic Components of Hops and Beer
Abstract
The value of hops (Humulus lupulus L.) in beer production has been undisputed for centuries. Hops is rich in humulones and lupulones which gives the characteristic aroma and bitter taste, and preserves this golden drink against growing bacteria and molds. Besides α- and β-acids, the lupulin glands of hop cones excrete prenylated flavonoids, which exhibit a broad spectrum of biological activities and therefore has therapeutic potential in humans. Recently, interest in hops was raised due to hop prenylated flavanones which show extraordinary estrogen activities. The strongest known phytoestrogen so far is 8-prenylnaringenin (8-PN), which along with 6-prenylanaringenin (6-PN), 6,8-diprenylnaringenin (6,8-DPN) and 8-geranylnaringenin (8-GN) are fundamental for the potent estrogen activity of hops. This review provides insight into the unusual hop phytoestrogens and shows numerous health benefits associated with their wide spectrum of biological activities including estrogenic, anticancer, neuropreventive, antinflamatory, and antimicrobial properties, which were intensively studied, and potential applications of these compounds such as, as an alternative to hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
Keywords: beer; biological activities; hop; phytoestrogens; prenylflavonoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

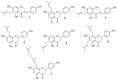

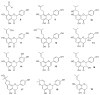

References
-
- Humulus lupulus | International Plant Names Index. [(accessed on 1 July 2020)]; Available online: https://www.ipni.org/n/303502-2.
-
- Koetter U., Biendl M. Hops (Humulus lupulus): A Review of its Historic and Medicinal Uses. J. Am. Bot. Counc. 2010;87:44–57.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

