Matrix Metalloproteinases and Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinases in Extracellular Matrix Remodeling during Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction and Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 32937927
- PMCID: PMC7555240
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21186742
Matrix Metalloproteinases and Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinases in Extracellular Matrix Remodeling during Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction and Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
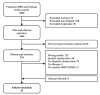
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) are pivotal regulators of extracellular matrix (ECM) composition and could, due to their dynamic activity, function as prognostic tools for fibrosis and cardiac function in left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). We conducted a systematic review on experimental animal models of LVDD and HFpEF published in MEDLINE or Embase. Twenty-three studies were included with a total of 36 comparisons that reported established LVDD, quantification of cardiac fibrosis and cardiac MMP or TIMP expression or activity. LVDD/HFpEF models were divided based on underlying pathology: hemodynamic overload (17 comparisons), metabolic alteration (16 comparisons) or ageing (3 comparisons). Meta-analysis showed that echocardiographic parameters were not consistently altered in LVDD/HFpEF with invasive hemodynamic measurements better representing LVDD. Increased myocardial fibrotic area indicated comparable characteristics between hemodynamic and metabolic models. Regarding MMPs and TIMPs; MMP2 and MMP9 activity and protein and TIMP1 protein levels were mainly enhanced in hemodynamic models. In most cases only mRNA was assessed and there were no correlations between cardiac tissue and plasma levels. Female gender, a known risk factor for LVDD and HFpEF, was underrepresented. Novel studies should detail relevant model characteristics and focus on MMP and TIMP protein expression and activity to identify predictive circulating markers in cardiac ECM remodeling.
Keywords: animal models; extracellular matrix; fibrosis; heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; left ventricular diastolic dysfunction; matrix metalloproteinase; systematic review; tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Kloch-Badelek M., Kuznetsova T., Sakiewicz W., Tikhonoff V., Ryabikov A., Gonzalez A., Lopez B., Thijs L., Jin Y., Malyutina S., et al. Prevalence of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in European populations based on cross-validated diagnostic thresholds. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound. 2012;10:10. doi: 10.1186/1476-7120-10-10. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rasmussen-Torvik L.J., Colangelo L.A., Lima J.A.C., Jacobs D.R., Rodriguez C.J., Gidding S.S., Lloyd-Jones D.M., Shah S.J. Prevalence and predictors of diastolic dysfunction according to different classification criteria: The coronary artery risk development in young in adults study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017;185:1221–1227. doi: 10.1093/aje/kww214. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Palmiero P., Zito A., Maiello M., Cameli M., Modesti P.A., Muiesan M.L., Novo S., Saba P.S., Scicchitano P., Pedrinelli R., et al. Left ventricular diastolic function in hypertension: Methodological considerations and clinical implications. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2015;7:137–144. doi: 10.14740/jocmr2050w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nagueh S.F., Smiseth O.A., Appleton C.P., Byrd B.F., Dokainish H., Edvardsen T., Flachskampf F.A., Gillebert T.C., Klein A.L., Lancellotti P., et al. Recommendations for the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography: An update from the american society of echocardiography and the european association of cardiovascular imaging. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2016;17:1321–1360. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jew082. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

