AGL15 Controls the Embryogenic Reprogramming of Somatic Cells in Arabidopsis through the Histone Acetylation-Mediated Repression of the miRNA Biogenesis Genes
- PMID: 32937992
- PMCID: PMC7554740
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21186733
AGL15 Controls the Embryogenic Reprogramming of Somatic Cells in Arabidopsis through the Histone Acetylation-Mediated Repression of the miRNA Biogenesis Genes
Abstract
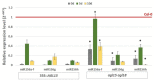
The embryogenic transition of somatic cells requires an extensive reprogramming of the cell transcriptome. Relevantly, the extensive modulation of the genes that have a regulatory function, in particular the genes encoding the transcription factors (TFs) and miRNAs, have been indicated as controlling somatic embryogenesis (SE) that is induced in vitro in the somatic cells of plants. Identifying the regulatory relationships between the TFs and miRNAs during SE induction is of central importance for understanding the complex regulatory interplay that fine-tunes a cell transcriptome during the embryogenic transition. Hence, here, we analysed the regulatory relationships between AGL15 (AGAMOUS-LIKE 15) TF and miR156 in an embryogenic culture of Arabidopsis. Both AGL15 and miR156 control SE induction and AGL15 has been reported to target the MIR156 genes in planta. The results showed that AGL15 contributes to the regulation of miR156 in an embryogenic culture at two levels that involve the activation of the MIR156 transcription and the containment of the abundance of mature miR156 by repressing the miRNA biogenesis genes DCL1 (DICER-LIKE1), SERRATE and HEN1 (HUA-ENHANCER1). To repress the miRNA biogenesis genes AGL15 seems to co-operate with the TOPLESS co-repressors (TPL and TPR1-4), which are components of the SIN3/HDAC silencing complex. The impact of TSA (trichostatin A), an inhibitor of the HDAC histone deacetylases, on the expression of the miRNA biogenesis genes together with the ChIP results implies that histone deacetylation is involved in the AGL15-mediated repression of miRNA processing. The results indicate that HDAC6 and HDAC19 histone deacetylases might co-operate with AGL15 in silencing the complex that controls the abundance of miR156 during embryogenic induction. This study provides new evidence about the histone acetylation-mediated control of the miRNA pathways during the embryogenic reprogramming of plant somatic cells and the essential role of AGL15 in this regulatory mechanism.
Keywords: AGL15; DCL1; HDAC; HEN1; SERRATE; TOPLESS co-repressor; acetylation; miR156; miRNA biogenesis; somatic embryogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Singla B., Tyagi A.K., Khurana J.P., Khurana P. Analysis of expression profile of selected genes expressed during auxin-induced somatic embryogenesis in leaf base system of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and their possible interactions. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007;65:677–692. doi: 10.1007/s11103-007-9234-z. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

