Cultural adaptation of the mental health first aid guidelines for assisting a person at risk of suicide to China: a Delphi expert consensus study
- PMID: 32938412
- PMCID: PMC7493309
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-020-02858-9
Cultural adaptation of the mental health first aid guidelines for assisting a person at risk of suicide to China: a Delphi expert consensus study
Abstract
Background: Suicide is a significant public health concern in China and there is a need for evidence-based suicide prevention programs to assist people in the community who may be in a position to support those in their social networks who are at risk of suicide. English-language mental health first aid guidelines for this purpose have been developed. However, due to differences in culture, language and health systems, guidelines for English-speaking countries require cultural adaptation for use in China.
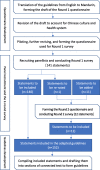
Methods: A Delphi expert consensus study was conducted among mainland Chinese panellists with a diverse range of expertise in suicide crisis intervention (n = 56). Using the mental health first aid guidelines used in English-speaking countries as a basis, a questionnaire containing 141 statements on how to help a person at risk of suicide was developed and translated. Panellists were asked to rate the importance of each item for inclusion in the Chinese guidelines. They were also encouraged to suggest any additional statements that were not included in the original questionnaire. Statements were accepted for inclusion in the adapted guidelines if they were endorsed by at least 80% of panellists as essential or important.
Results: Consensus was achieved after two survey rounds on 152 statements for inclusion in the adapted guidelines for China, with 141 adopted from the guidelines for English-speaking countries and 11 generated from the comments of panellists.
Conclusions: While the adapted guidelines were similar to the guidelines for English-speaking countries, they also incorporated actions specific to the Chinese context, including Chinese attitudes towards suicide, the role of families and friends and removal of the means of suicide. Further research is needed to investigate the use of the guidelines by the Chinese public and the implementation of Mental Health First Aid training in appropriate settings in China.
Keywords: China; Cultural adaptation; Delphi study; Mental health first aid; Suicide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Development of Chinese mental health first aid guidelines for assisting a person affected by a traumatic event: a Delphi expert consensus study.BMC Psychiatry. 2021 Dec 1;21(1):600. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03606-3. BMC Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34852789 Free PMC article.
-
Cultural adaptation of the mental health first aid guidelines for depression used in English-speaking countries for China: a Delphi expert consensus study.BMC Psychiatry. 2020 Jun 26;20(1):336. doi: 10.1186/s12888-020-02736-4. BMC Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32586291 Free PMC article.
-
Cultural adaptation of the mental health first aid guidelines for assisting a person at risk of suicide for Sri Lanka: a Delphi expert consensus study.BMC Psychiatry. 2021 Sep 24;21(1):466. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03486-7. BMC Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34560861 Free PMC article.
-
Providing mental health first aid in the workplace: a Delphi consensus study.BMC Psychol. 2016 Aug 2;4(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s40359-016-0148-x. BMC Psychol. 2016. PMID: 27485609 Free PMC article.
-
Re-development of mental health first aid guidelines for suicidal ideation and behaviour: a Delphi study.BMC Psychiatry. 2014 Sep 13;14:241. doi: 10.1186/s12888-014-0241-8. BMC Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25213799 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Development of mental health first-aid guidelines for suicide risk: a Delphi expert consensus study in Argentina and Chile.BMC Psychiatry. 2023 Dec 11;23(1):928. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-05417-0. BMC Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 38082256 Free PMC article.
-
Development of the Life Gatekeeper suicide prevention training programme in China: a Delphi study.Gen Psychiatr. 2023 Oct 17;36(5):e101133. doi: 10.1136/gpsych-2023-101133. eCollection 2023. Gen Psychiatr. 2023. PMID: 37859750 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of the meaning in life and suicidal ideation based on Chinese samples.Front Psychol. 2025 Aug 1;16:1610351. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1610351. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40823416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adapting the depression component of WHO Mental Health Gap Intervention Guide (mhGAP-IG.v2) for primary care in Shenzhen, China: a DELPHI study.Int J Ment Health Syst. 2022 Feb 15;16(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13033-022-00523-0. Int J Ment Health Syst. 2022. PMID: 35168656 Free PMC article.
-
Cultural adaptation of the mental health first aid guidelines for Brazilians with problem drinking: a Delphi expert consensus study.BMC Psychiatry. 2022 Mar 7;22(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12888-022-03709-5. BMC Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35255851 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organisation. Preventing suicide: a global imperative. 2014.
-
- Cerel J, Brown MM, Maple M, Singleton M, van de Venne J, Moore M, Flaherty C. How many people are exposed to suicide? Not Six. Suicide Life Threat Behav. 2019;49(2):529–534. - PubMed
-
- Hsu CY, O'Connor M, Lee S. Understandings of death and dying for people of Chinese origin. Death Stud. 2009;33(2):153–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical