RAD51: Beyond the break
- PMID: 32938550
- PMCID: PMC8082279
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.08.010
RAD51: Beyond the break
Abstract
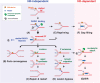
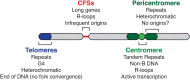
As the primary catalyst of homologous recombination (HR) in vertebrates, RAD51 has been extensively studied in the context of repair of double-stranded DNA breaks (DSBs). With recent advances in the understanding of RAD51 function extending beyond DSBs, the importance of RAD51 throughout DNA metabolism has become increasingly clear. Here we review the suggested roles of RAD51 beyond HR, specifically focusing on their interplay with DNA replication and the maintenance of genomic stability, in which RAD51 function emerges as a double-edged sword.
Keywords: Double-stranded DNA breaks; Fork protection; Homologous recombination; RAD51; Replicative stress.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Richardson C., Jasin M. Frequent chromosomal translocations induced by DNA double-strand breaks. Nature. 2000;405:697–700. - PubMed
-
- Vamvakas S., Vock E.H., Lutz W.K. On the role of DNA double-strand breaks in toxicity and carcinogenesis. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1997;27:155–174. - PubMed
-
- Baumann P., West S.C. Role of the human RAD51 protein in homologous recombination and double-stranded-break repair. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998;23:247–251. - PubMed
-
- Stark J.M., Hu P., Pierce A.J., Moynahan M.E., Ellis N., Jasin M. ATP hydrolysis by mammalian RAD51 has a key role during homology-directed DNA repair. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:20185–20194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

