Validation of a survival-risk score (SRS) in relapsed/refractory CLL patients treated with idelalisib-rituximab
- PMID: 32938904
- PMCID: PMC7494850
- DOI: 10.1038/s41408-020-00358-3
Validation of a survival-risk score (SRS) in relapsed/refractory CLL patients treated with idelalisib-rituximab
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
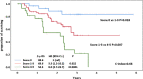
Figures
References
-
- Gentile M, et al. Survival-risk score for real-life relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients receiving ibrutinib. A Campus CLL study. Leukemia10.1038/s41375-020-0833-x. (2020) [Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
-
- Soumerai JD, et al. Prognostic risk score for patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia treated with targeted therapies or chemoimmunotherapy: a retrospective, pooled cohort study with external validations. Lancet Haematol. 2019;6:e366–e374. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(19)30085-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

