PKC-δ deficiency in B cells displays osteopenia accompanied with upregulation of RANKL expression and osteoclast-osteoblast uncoupling
- PMID: 32938907
- PMCID: PMC7494897
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-02947-3
PKC-δ deficiency in B cells displays osteopenia accompanied with upregulation of RANKL expression and osteoclast-osteoblast uncoupling
Abstract
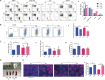
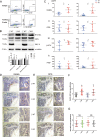
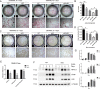
PKC-δ is an important molecule for B-cell proliferation and tolerance. B cells have long been recognized to play a part in osteoimmunology and pathological bone loss. However, the role of B cells with PKC-δ deficiency in bone homeostasis and the underlying mechanisms are unknown. We generated mice with PKC-δ deletion selectively in B cells by crossing PKC-δ-loxP mice with CD19-Cre mice. We studied their bone phenotype using micro-CT and histology. Next, immune organs were obtained and analyzed. Western blotting was used to determine the RANKL/OPG ratio in vitro in B-cell cultures, ELISA assay and immunohistochemistry were used to analyze in vivo RANKL/OPG balance in serum and bone sections respectively. Finally, we utilized osteoclastogenesis to study osteoclast function via hydroxyapatite resorption assay, and isolated primary calvaria osteoblasts to investigate osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. We also investigated osteoclast and osteoblast biology in co-culture with B-cell supernatants. We found that mice with PKC-δ deficiency in B cells displayed an osteopenia phenotype in the trabecular and cortical compartment of long bones. In addition, PKC-δ deletion resulted in changes of trabecular bone structure in association with activation of osteoclast bone resorption and decrease in osteoblast parameters. As expected, inactivation of PKC-δ in B cells resulted in changes in spleen B-cell number, function, and distribution. Consistently, the RANKL/OPG ratio was elevated remarkably in B-cell culture, in the serum and in bone specimens after loss of PKC-δ in B cells. Finally, in vitro analysis revealed that PKC-δ ablation suppressed osteoclast differentiation and function but co-culture with B-cell supernatant reversed the suppression effect, as well as impaired osteoblast proliferation and function, indicative of osteoclast-osteoblast uncoupling. In conclusion, PKC-δ plays an important role in the interplay between B cells in the immune system and bone cells in the pathogenesis of bone lytic diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

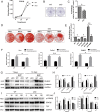
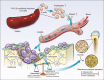
Similar articles
-
The roles of TNFR1 in lipopolysaccharide-induced bone loss: dual effects of TNFR1 on bone metabolism via osteoclastogenesis and osteoblast survival.J Orthop Res. 2010 May;28(5):657-63. doi: 10.1002/jor.21028. J Orthop Res. 2010. PMID: 19890995
-
Estrogens antagonize RUNX2-mediated osteoblast-driven osteoclastogenesis through regulating RANKL membrane association.Bone. 2015 Jun;75:96-104. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.02.007. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Bone. 2015. PMID: 25701138 Free PMC article.
-
Aging increases stromal/osteoblastic cell-induced osteoclastogenesis and alters the osteoclast precursor pool in the mouse.J Bone Miner Res. 2005 Sep;20(9):1659-68. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.050503. Epub 2005 May 2. J Bone Miner Res. 2005. PMID: 16059637
-
Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways.J Bone Miner Metab. 2021 Jan;39(1):19-26. doi: 10.1007/s00774-020-01162-6. Epub 2020 Oct 20. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021. PMID: 33079279 Review.
-
Probiotics and bone disorders: the role of RANKL/RANK/OPG pathway.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020 Mar;32(3):363-371. doi: 10.1007/s40520-019-01223-5. Epub 2019 May 22. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020. PMID: 31119697 Review.
Cited by
-
Abnormal upregulation of NUBP2 contributes to cancer progression in colorectal cancer.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jan;480(1):399-410. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-04956-8. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 38492158 Free PMC article.
-
Sending the Signal to Bone: How Tumor-Derived EVs Orchestrate Pre-Metastatic Niche Formation and Skeletal Colonization.Biomedicines. 2025 Jul 4;13(7):1640. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13071640. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40722712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen-mediated downregulation of HIF-1α signaling in B lymphocytes influences postmenopausal bone loss.Bone Res. 2022 Feb 17;10(1):15. doi: 10.1038/s41413-022-00189-x. Bone Res. 2022. PMID: 35177582 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of B-lymphocytes and bone cells in health and disease.Bone. 2023 Mar;168:116296. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2021.116296. Epub 2021 Dec 21. Bone. 2023. PMID: 34942359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antidementia medication acetylcholinesterase inhibitors have therapeutic benefits on osteoporotic bone by attenuating osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption.J Cell Physiol. 2023 Aug;238(8):1823-1835. doi: 10.1002/jcp.31057. Epub 2023 Jun 19. J Cell Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37334837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arron JR, Choi Y. Bone versus immune system. Nature. 2000;408:535–536. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

