Neonatal Gastric Perforation: Our Experience and Important Preoperative and Intraoperative Caveats to Prognosticate and Improve Survival
- PMID: 32939110
- PMCID: PMC7478279
- DOI: 10.4103/jiaps.JIAPS_80_19
Neonatal Gastric Perforation: Our Experience and Important Preoperative and Intraoperative Caveats to Prognosticate and Improve Survival
Abstract
Aim: Neonatal gastric perforation (NGP) is a rare, perplexing, life-threatening entity affecting neonates. We share our experience of operating upon cases of NGP s and highlight important points observed which may aid in further improving care of neonates, diagnosed with this entity.
Materials and methods: A retrospective analysis of all consecutive patients with NGP operated by the author, at various centers between January 2015 and December 2018, was carried out. We analyzed different variables for these and reached logical conclusions.
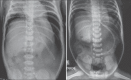
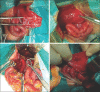
Results: Between January 2015 and December 2018, we treated ten patients with gastric perforation. All the neonates were preterm, except one. Mean birth weight in our series was 1745 g (range 1300-2400 g). Deterioration in activity, worsening of sepsis, metabolic acidosis, increased ventilator requirements, and abdominal distension were prominent clinical features identified in all patients. All patients subsequently had massive pneumoperitoneum before surgery. Six patients had perforation along the greater curvature, two had perforation at the posterior wall, and two had near total gastric necrosis. We had four mortalities out of ten patients operated.
Conclusion: NGP is associated with high mortality, especially in premature and low birth weight neonates. Severity of contributing factors in a premature predisposed neonate determines the severity of gastric necrosis, which in turn is an important prognostic factor. Certain preoperative signs can be useful and can aid in initiating preventive measures to curtail severity of the pathology.
Keywords: Gastric necrosis; gastrorrhaphy; neonatal gastric perforation.
Copyright: © 2020 Journal of Indian Association of Pediatric Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neonatal Gastric Perforation: 14-Year Experience from a Tertiary Neonatal Intensive Care Unit.Am J Perinatol. 2023 Jul;40(10):1112-1118. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1733780. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Am J Perinatol. 2023. PMID: 34327684
-
Pathogenetic and Prognostic Factors for Neonatal Gastric Perforation: Personal Experience and Systematic Review of the Literature.Front Pediatr. 2018 Apr 4;6:61. doi: 10.3389/fped.2018.00061. eCollection 2018. Front Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 29670869 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal gastric perforation: A single center experience.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2014 Aug 27;6(8):151-5. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v6.i8.151. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2014. PMID: 25161763 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal gastric perforation: a report of two cases and a systematic review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Apr;97(17):e0369. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010369. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29702982 Free PMC article.
-
Etiology of neonatal gastric perforations: review of 10 years' experience.Pediatr Int. 2007 Oct;49(5):626-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200X.2007.02427.x. Pediatr Int. 2007. PMID: 17875089 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of early postoperative enteral nutrition on the short-term prognosis in neonatal gastric perforation.Pediatr Discov. 2023 Oct 18;3(1):e34. doi: 10.1002/pdi3.34. eCollection 2025 Mar. Pediatr Discov. 2023. PMID: 40626297 Free PMC article.
-
Sleeve gastrectomy for multiple gastric perforations in a preterm: A case report.Clin Case Rep. 2022 Nov 23;10(11):e6541. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.6541. eCollection 2022 Nov. Clin Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36439389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang T, Huang Y, Li J, Zhong W, Tan T, Yu J, et al. Neonatal gastric perforation: Case series and literature review. World J Surg. 2018;42:2668–73. - PubMed
-
- Babayigit A, Ozaydın S, Cetinkaya M, Sander S. Neonatal gastric perforations in very low birth weight infants: A single center experience and review of the literature. Pediatr Surg Int. 2018;34:79–84. - PubMed
-
- Leone RJ, Jr, Krasna IH. 'Spontaneous' neonatal gastric perforation: Is it really spontaneous? J Pediatr Surg. 2000;35:1066–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources