Early detection and treatment of complications in the fingers and hand after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair
- PMID: 32939495
- PMCID: PMC7479023
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jseint.2020.04.025
Early detection and treatment of complications in the fingers and hand after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair
Abstract
Background: Complications in the fingers and hand after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair (ARCR) have been reported to include carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), flexor tenosynovitis (TS), and complex regional pain syndrome. These studies were conducted retrospectively; however, the reported complications have not been examined prospectively. The aim of this study was to evaluate the outcomes of early detection and treatment of the complications after ARCR.
Methods: Forty-six patients (48 shoulders) who underwent ARCR were prospectively examined to investigate complications in the fingers and hand after ARCR. We attempted to immediately detect and proactively treat these complications. We evaluated the outcomes of the early detection and treatment of the complications.
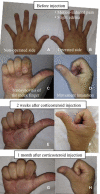
Results: Complications were observed in 17 hands (35%) and occurred an average of 1.5 months after ARCR. The symptoms in 3 hands resolved spontaneously, 2 hands were diagnosed with CTS, and 12 hands were diagnosed with TS. Of the 12 hands with TS, 11 exhibited no triggering of the fingers. Among the 14 hands diagnosed with CTS or TS, 13 hands (CTS: 2 hands, TS: 11 hands) were treated with corticosteroid injections; the mean interval between treatment initiation and symptom resolution was 1.0 months (0.5-3.0 months). None exhibited complex regional pain syndrome.
Conclusions: When symptoms occur in the fingers and hand after ARCR, CTS or TS should be primarily suspected. The diagnosis of TS must be made carefully because most patients with TS have no triggering. For patients with CTS or TS after ARCR, rapid corticosteroid injection administration can lead to improvement in these symptoms.
Keywords: Shoulder; arthroscopic rotator cuff repair; carpal tunnel syndrome; complex regional pain syndrome; finger; flexor tenosynovitis; hand; trigger finger.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Risk factors related to complications of the fingers and hand after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair - carpal tunnel syndrome, flexor tenosynovitis, and complex regional pain syndrome.JSES Int. 2021 Aug 30;5(6):1077-1085. doi: 10.1016/j.jseint.2021.07.001. eCollection 2021 Nov. JSES Int. 2021. PMID: 34766088 Free PMC article.
-
Complications of the Fingers and Hand After Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair.Open Orthop J. 2018 Mar 30;12:134-140. doi: 10.2174/1874325001812010134. eCollection 2018. Open Orthop J. 2018. PMID: 29785223 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Modeling to Determine Functional Outcomes After Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair.Am J Sports Med. 2020 Jun;48(7):1559-1567. doi: 10.1177/0363546520914632. Epub 2020 May 14. Am J Sports Med. 2020. PMID: 32406765
-
Complications associated with arthroscopic rotator cuff tear repair: definition of a core event set by Delphi consensus process.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016 Dec;25(12):1907-1917. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2016.04.036. Epub 2016 Aug 2. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016. PMID: 27496354
-
The Evolution of Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair.Orthop J Sports Med. 2021 Dec 6;9(12):23259671211050899. doi: 10.1177/23259671211050899. eCollection 2021 Dec. Orthop J Sports Med. 2021. PMID: 34901288 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Postoperative Pathologies of the Hand Following Shoulder Surgery.J Hand Surg Glob Online. 2024 Jul 31;6(5):645-649. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsg.2024.05.011. eCollection 2024 Sep. J Hand Surg Glob Online. 2024. PMID: 39381393 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors related to complications of the fingers and hand after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair - carpal tunnel syndrome, flexor tenosynovitis, and complex regional pain syndrome.JSES Int. 2021 Aug 30;5(6):1077-1085. doi: 10.1016/j.jseint.2021.07.001. eCollection 2021 Nov. JSES Int. 2021. PMID: 34766088 Free PMC article.
-
The Incidence of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Diagnosis Increases after Arthroscopic Shoulder Surgery.J Hand Surg Glob Online. 2023 Jun 6;5(5):624-629. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsg.2023.05.005. eCollection 2023 Sep. J Hand Surg Glob Online. 2023. PMID: 37790837 Free PMC article.
-
Iatrogenic Ulnar Nerve Neuropathy Following Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Electrodiagnostic Findings in 18 Patients.Cureus. 2023 May 16;15(5):e39089. doi: 10.7759/cureus.39089. eCollection 2023 May. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37378144 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical outcome in patients with hand lesions associated with complex regional pain syndrome after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair.Clin Shoulder Elb. 2021 Jun;24(2):80-87. doi: 10.5397/cise.2021.00080. Epub 2021 May 18. Clin Shoulder Elb. 2021. PMID: 34078015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonnici A.V., Spencer J.D. A survey of ‘trigger finger’ in adults. J Hand Surg Br. 1988;13:202–203. - PubMed
-
- Bruehl S., Harden R.N., Galer B.S., Saltz S., Bertram M., Backonja M. External validation of IASP diagnostic criteria for complex regional pain syndrome and proposed research diagnostic criteria. International Association for the Study of Pain. Pain. 1999;81:147–154. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
