Trophoblastic extracellular vesicles and viruses: Friends or foes?
- PMID: 32939907
- PMCID: PMC7880881
- DOI: 10.1111/aji.13345
Trophoblastic extracellular vesicles and viruses: Friends or foes?
Abstract
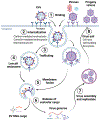
Cells produce cytoplasmic vesicles to facilitate the processing and transport of RNAs, proteins, and other signaling molecules among intracellular organelles. Moreover, most cells release a range of extracellular vesicles (EVs) that mediate intercellular communication in both physiological and pathological settings. In addition to a better understanding of their biological functions, the diagnostic and therapeutic prospects of EVs, particularly the nano-sized small EVs (sEVs, exosomes), are currently being rigorously pursued. While EVs and viruses such as retroviruses might have evolved independently, they share a number of similar characteristics, including biogenesis pathways, size distribution, cargo, and cell-targeting mechanisms. The interplay of EVs with viruses has profound effects on viral replication and infectivity. Our research indicates that sEVs, produced by primary human trophoblasts, can endow other non-placental cell types with antiviral response. Better insights into the interaction of EVs with viruses may illuminate new ways to attenuate viral infections during pregnancy, and perhaps develop new antiviral therapeutics to protect the feto-placental unit during critical times of human development.
Keywords: Placenta; extracellular vesicles; microRNA; trophoblast; viruses.
© 2020 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular vesicles in embryo implantation and disorders of the endometrium.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2021 Feb;85(2):e13360. doi: 10.1111/aji.13360. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33064348 Review.
-
Isolation of human trophoblastic extracellular vesicles and characterization of their cargo and antiviral activity.Placenta. 2016 Nov;47:86-95. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2016.09.008. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Placenta. 2016. PMID: 27780544 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory properties of extracellular vesicles in the dialogue between placental and immune cells.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2021 Feb;85(2):e13383. doi: 10.1111/aji.13383. Epub 2020 Dec 27. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33251688 Review.
-
Chromosome 19 microRNAs exert antiviral activity independent from type III interferon signaling.Placenta. 2018 Jan;61:33-38. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2017.11.004. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Placenta. 2018. PMID: 29277269 Free PMC article.
-
Murine trophoblast-derived and pregnancy-associated exosome-enriched extracellular vesicle microRNAs: Implications for placenta driven effects on maternal physiology.PLoS One. 2019 Feb 7;14(2):e0210675. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210675. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30730971 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Small extracellular vesicles from plasma of women with preeclampsia increase myogenic tone and decrease endothelium-dependent relaxation of mouse mesenteric arteries.Pregnancy Hypertens. 2022 Jun;28:66-73. doi: 10.1016/j.preghy.2022.02.005. Epub 2022 Feb 19. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2022. PMID: 35240546 Free PMC article.
-
Micro Trojan horses: Engineering extracellular vesicles crossing biological barriers for drug delivery.Bioeng Transl Med. 2024 Jan 11;9(2):e10623. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10623. eCollection 2024 Mar. Bioeng Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38435823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles and immune response during pregnancy: A balancing act.Immunol Rev. 2022 Jul;308(1):105-122. doi: 10.1111/imr.13074. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Immunol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35199366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs: the architects of placental development and pregnancy success.Mol Genet Genomics. 2025 Mar 30;300(1):39. doi: 10.1007/s00438-025-02244-8. Mol Genet Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40159439 Review.
-
Placenta-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Pregnancy Complications and Prospects on a Liquid Biopsy for Hemoglobin Bart's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 16;24(6):5658. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065658. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982732 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Murillo OD, Thistlethwaite W, Rozowsky J, Subramanian SL, Lucero R, Shah N, Jackson AR, Srinivasan S, Chung A, Laurent CD, Kitchen RR, Galeev T, Warrell J, Diao JA, Welsh JA, Hanspers K, Riutta A, Burgstaller-Muehlbacher S, Shah RV, Yeri A, Jenkins LM, Ahsen ME, Cordon-Cardo C, Dogra N, Gifford SM, Smith JT, Stolovitzky G, Tewari AK, Wunsch BH, Yadav KK, Danielson KM, Filant J, Moeller C, Nejad P, Paul A, Simonson B, Wong DK, Zhang X, Balaj L, Gandhi R, Sood AK, Alexander RP, Wang L, Wu C, Wong DTW, Galas DJ, Van Keuren-Jensen K, Patel T, Jones JC, Das S, Cheung KH, Pico AR, Su AI, Raffai RL, Laurent LC, Roth ME, Gerstein MB, Milosavljevic A. exRNA atlas analysis reveals distinct extracellular RNA cargo types and their carriers present across human biofluids. Cell. 2019;177(2):463–477.e15. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Srinivasan S, Yeri A, Cheah PS, Chung A, Danielson K, De Hoff P, Filant J, Laurent CD, Laurent LD, Magee R, Moeller C, Murthy VL, Nejad P, Paul A, Rigoutsos I, Rodosthenous R, Shah RV, Simonson B, To C, Wong D, Yan IK, Zhang X, Balaj L, Breakefield XO, Daaboul G, Gandhi R, Lapidus J, Londin E, Patel T, Raffai RL, Sood AK, Alexander RP, Das S, Laurent LC. Small RNA Sequencing across diverse biofluids identifies optimal methods for exRNA isolation. Cell. 2019;177(2):446–462.e16. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

