First In-Human Burst Wave Lithotripsy for Kidney Stone Comminution: Initial Two Case Studies
- PMID: 32940089
- PMCID: PMC8080914
- DOI: 10.1089/end.2020.0725
First In-Human Burst Wave Lithotripsy for Kidney Stone Comminution: Initial Two Case Studies
Abstract
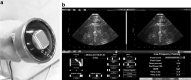
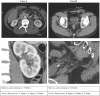
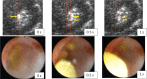
Purpose: To test the effectiveness (Participant A) and tolerability (Participant B) of urinary stone comminution in the first-in-human trial of a new technology, burst-wave lithotripsy (BWL). Materials and Methods: An investigational BWL and ultrasonic propulsion system was used to target a 7-mm kidney stone in the operating room before ureteroscopy (Participant A). The same system was used to target a 7.5 mm ureterovesical junction stone in clinic without anesthesia (Participant B). Results: For Participant A, a ureteroscope inserted after 9 minutes of BWL observed fragmentation of the stone to <2 mm fragments. Participant B tolerated the procedure without pain from BWL, required no anesthesia, and passed the stone on day 15. Conclusions: The first-in-human tests of BWL pulses were successful in that a renal stone was comminuted in <10 minutes, and BWL was also tolerated by an awake subject for a distal ureteral stone. Clinical Trial NCT03873259 and NCT02028559.
Keywords: burst wave lithotripsy; calculi; lithotripsy; physics; shock wave lithotripsy; ultrasound; urolithiasis.
Conflict of interest statement
A.D.M., B.W.C., B.D., M.R.B., and M.D.S. have consulting agreements with and equity in SonoMotion, Inc., which has licensed this technology from the University of Washington.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fragmentation of Stones by Burst Wave Lithotripsy in the First 19 Humans.J Urol. 2022 May;207(5):1067-1076. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000002446. Epub 2022 Mar 21. J Urol. 2022. PMID: 35311351 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Burst Wave Lithotripsy and Ultrasonic Propulsion for Improved Urinary Stone Fragmentation.J Endourol. 2018 Apr;32(4):344-349. doi: 10.1089/end.2017.0675. Epub 2018 Mar 20. J Endourol. 2018. PMID: 29433329 Free PMC article.
-
Application of novel burst wave lithotripsy and ultrasonic propulsion technology for the treatment of ureteral calculi in a bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) and renal calculi in a harbor seal (Phoca vitulina).Urolithiasis. 2024 Jan 8;52(1):21. doi: 10.1007/s00240-023-01515-6. Urolithiasis. 2024. PMID: 38189835 Free PMC article.
-
Burst wave lithotripsy - a paradigm shift: inferences from a scoping review.World J Urol. 2025 Apr 25;43(1):250. doi: 10.1007/s00345-025-05645-x. World J Urol. 2025. PMID: 40278907 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of Flexible Ureteroscopy vs Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy for Renal Stones in Pediatric Patients: A European Association of Urology Urolithiasis Guidelines Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Urol. 2023 Dec;210(6):876-887. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000003696. Epub 2023 Sep 5. J Urol. 2023. PMID: 37669621
Cited by
-
First Series Using Ultrasonic Propulsion and Burst Wave Lithotripsy to Treat Ureteral Stones.J Urol. 2022 Nov;208(5):1075-1082. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000002864. Epub 2022 Nov 1. J Urol. 2022. PMID: 36205340 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a burst wave lithotripsy system for noninvasive fragmentation of ureteroliths in pet cats.BMC Vet Res. 2023 Sep 2;19(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s12917-023-03705-1. BMC Vet Res. 2023. PMID: 37660015 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Science of Burst Wave Lithotripsy and Ultrasonic Propulsion.BME Front. 2022;2022:9847952. doi: 10.34133/2022/9847952. Epub 2022 Feb 17. BME Front. 2022. PMID: 37090444 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and Morphological Changes Associated with Burst Wave Lithotripsy-Treated Pig Kidneys.J Endourol. 2022 Dec;36(12):1580-1585. doi: 10.1089/end.2022.0295. Epub 2022 Sep 5. J Endourol. 2022. PMID: 35920117 Free PMC article.
-
Fragmentation of Stones by Burst Wave Lithotripsy in the First 19 Humans.J Urol. 2022 May;207(5):1067-1076. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000002446. Epub 2022 Mar 21. J Urol. 2022. PMID: 35311351 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

