Seroprevalence of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in residents of Karachi-challenges in acquiring herd immunity for COVID 19
- PMID: 32940328
- PMCID: PMC7797721
- DOI: 10.1093/pubmed/fdaa170
Seroprevalence of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in residents of Karachi-challenges in acquiring herd immunity for COVID 19
Abstract
Background: The recent pandemic by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a global emergency. There is large number of asymptomatic cases of SARS-CoV-2 that are not reported. Hence, serological evidence of SARS-CoV2 antibodies is warranted for a better estimation of the actual number of infected patients to limit the disease spread and to get an idea of herd immunity.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study conducted from May 2020 to July 2020 at National Institute of Blood Diseases at Pakistan. The study includes healthcare workers (HCWs), community and industrial workers. The anti-SARS-CoV-2 test was performed by electrochemiluminescence immunoassay analyzer.
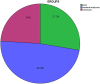
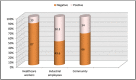
Results: A total of 1675 samples have been received from three groups of population. The percentage positivity for industrial employees is high (50.3%) for HCW (13.2%) and community population (34%).Total percentage for positive antibodies result is ~36%.
Conclusion: Our seroprevalence is 36%, which still far from herd immunity that needs to be at least 60-70% in population. If we consider acquiring 60% seroprevalence in next few months, then herd immunity is not far from reality, provided the antibodies did not decline with time. Although the current study is based on a small sample of participants, the findings suggest a study with larger population to implement stronger and targeted interventions.
Keywords: infectious disease; public health.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Faculty of Public Health. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Unhale SS, Ansar QB, Sanap S et al. . A review on corona virus (Covid-19). World J Pharm Life Sci 2020;6(4):109–15.
-
- Rodriguez-Morales AJ, Bonilla-Aldana DK, Tiwari R et al. . COVID-19, an emerging coronavirus infection: current scenario and recent developments-an overview. J Pure Appl Microbiol 2020;14:6150.
-
- Cascella M, Rajnik M, Cuomo A et al. . Features, Evaluation and Treatment Coronavirus (COVID-19) In Statpearls [internet] StatPearls Publishing, 2020. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous