Metformin Is Associated with Reduced Tissue Factor Procoagulant Activity in Patients with Poorly Controlled Diabetes
- PMID: 32940892
- PMCID: PMC8266708
- DOI: 10.1007/s10557-020-07040-7
Metformin Is Associated with Reduced Tissue Factor Procoagulant Activity in Patients with Poorly Controlled Diabetes
Abstract
Purpose: Metformin is the first-line antidiabetic drug and shown to reduce cardiovascular risk independent from its glucose lowering action. Particularly in poorly controlled diabetes, tissue factor (TF) is expressed in the vasculature and accounts for thromboembolic complications. Here, we aimed to assess the effect of metformin on TF activity and markers of vascular inflammation in poorly controlled type 2 diabetes.
Methods: In a cohort of patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes (glycosylated hemoglobin 8.39 ± 0.24%, 68.1 ± 2.6 mmol/mol, n = 46) of whom half of the individuals were treated with metformin and the other half did not receive metformin as part of an anti-diabetic combination therapy, we assessed TF activity and markers of vascular inflammation. In vitro, human monocytic cells (THP-1) were exposed to metformin and TF expression measured in the presence and absence of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activator 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside (AICAR) or the AMPK inhibitor compound C.
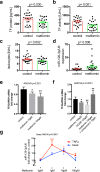
Results: In the patients, metformin treatment was associated with lower levels of TF protein (241.5 ± 19 vs. 315.4 ± 25 pg/mL, p = 0.03) and reduced TF activity (408.9 ± 49 vs. 643.8 ± 47 U/mL, p = 0.001) compared with controls. Moreover, the patients on metformin showed lower levels of vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM)1 (26.6 ± 1.4 vs. 35.03 ± 3.1 ng/mL, p = 0.014) and higher expression of miR-126-3p/U6sno (11.39 ± 2.8 vs. 4.26 ± 0.9, p = 0.006), a known post-transcriptional down regulator of TF and VCAM1. In vitro, metformin dose-dependently reduced lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced TF expression in THP-1 cells. The AMPK activator AICAR alone lowered TF expression in THP-1, while the AMPK inhibitor compound C abrogated the metformin-dependent reduction in TF expression.
Conclusions: Our data are the first to report that metformin is associated with reduced plasma TF procoagulant activity possibly explaining-at least in part-the vasculoprotective properties of metformin.
Keywords: Metformin; cardiovascular disease; coagulation; diabetes mellitus; microRNA; thrombosis; tissue factor; vascular complications; vascular inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vascular miR-181b controls tissue factor-dependent thrombogenicity and inflammation in type 2 diabetes.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Feb 17;19(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-0993-z. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32066445 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-19a contributes to the epigenetic regulation of tissue factor in diabetes.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018 Feb 24;17(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12933-018-0678-z. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018. PMID: 29477147 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of short-term treatment with metformin on markers of endothelial function and inflammatory activity in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial.J Intern Med. 2005 Jan;257(1):100-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2004.01420.x. J Intern Med. 2005. PMID: 15606381 Clinical Trial.
-
Glucose-lowering treatment of type 2 diabetes. Part II--Glucose-lowering drugs after metformin: a choice based largely on adverse effects.Prescrire Int. 2015 May;24(160):130-5. Prescrire Int. 2015. PMID: 26034806 Review.
-
Repaglinide : a pharmacoeconomic review of its use in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Pharmacoeconomics. 2004;22(6):389-411. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200422060-00005. Pharmacoeconomics. 2004. PMID: 15099124 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus on Coagulation and Hemostasis.J Clin Med. 2021 May 29;10(11):2419. doi: 10.3390/jcm10112419. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34072487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Comparison of Sulfonamide-Based Derivatives That Can Improve Anti-Coagulation Properties of Metformin.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 8;23(8):4132. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084132. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35456961 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of subclinical myocardial necrosis using high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T in patients with prediabetes.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Aug 21;20(1):171. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01365-9. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 34419046 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Biomarkers of Thrombo-Inflammation in Patients with First-Diagnosed Atrial Fibrillation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 8;25(7):4109. doi: 10.3390/ijms25074109. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612918 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of microRNAs as diagnostics and potential therapeutic interest in type 2 diabetes mellitus.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Jan 26;12(3):525-537. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i3.525. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 38322458 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

