Role of Skeletal Muscle in Insulin Resistance and Glucose Uptake
- PMID: 32940941
- PMCID: PMC8074531
- DOI: 10.1002/cphy.c190029
Role of Skeletal Muscle in Insulin Resistance and Glucose Uptake
Abstract
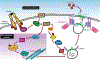
The skeletal muscle is the largest organ in the body, by mass. It is also the regulator of glucose homeostasis, responsible for 80% of postprandial glucose uptake from the circulation. Skeletal muscle is essential for metabolism, both for its role in glucose uptake and its importance in exercise and metabolic disease. In this article, we give an overview of the importance of skeletal muscle in metabolism, describing its role in glucose uptake and the diseases that are associated with skeletal muscle metabolic dysregulation. We focus on the role of skeletal muscle in peripheral insulin resistance and the potential for skeletal muscle-targeted therapeutics to combat insulin resistance and diabetes, as well as other metabolic diseases like aging and obesity. In particular, we outline the possibilities and pitfalls of the quest for exercise mimetics, which are intended to target the molecular mechanisms underlying the beneficial effects of exercise on metabolic disease. We also provide a description of the molecular mechanisms that regulate skeletal muscle glucose uptake, including a focus on the SNARE proteins, which are essential regulators of glucose transport into the skeletal muscle. © 2020 American Physiological Society. Compr Physiol 10:785-809, 2020.
Copyright © 2020 American Physiological Society. All rights reserved.
Figures

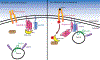

References
-
- Ahirwar AK, Jain A, Goswami B, Bhatnagar MK, Bhatacharjee J. Imbalance between protective (adiponectin) and prothrombotic (Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1) adipokines in metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab Syndr 8: 152–155, 2014. - PubMed
-
- Alessi DR, James SR, Downes CP, Holmes AB, Gaffney PR, Reese CB, Cohen P. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Balpha. Curr Biol 7: 261–269, 1997. - PubMed
-
- Almendro V, Busquets S, Ametller E, Carbo N, Figueras M, Fuster G, Argiles JM, Lopez-Soriano FJ. Effects of interleukin-15 on lipid oxidation: Disposal of an oral [(14)C]-triolein load. Biochim Biophys Acta 1761: 37–42, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

