Localized Cell-Surface Sampling of a Secreted Factor Using Cell-Targeting Beads
- PMID: 32941013
- PMCID: PMC8259888
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c02578
Localized Cell-Surface Sampling of a Secreted Factor Using Cell-Targeting Beads
Abstract
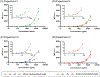
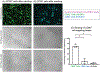
Intercellular communication through the secretion of soluble factors plays a vital role in a wide range of biological processes (e.g., homeostasis, immune response), yet identification and quantification of many of these factors can be challenging due to their degradation or sequestration in cell culture media prior to analysis. Here, we present a customizable bead-based system capable of simultaneously binding to live cells (through antibody-mediated cell tethering) and capturing cell-secreted molecules. Our functionalized beads capture secreted molecules (e.g., hepatocyte growth factor secreted by fibroblasts) that are diminished when sampled via traditional supernatant analysis techniques (p < 0.05), effectively rescuing a reduced signal in the presence of neutralizing components in the cell culture media. Our system enables capture and analysis of molecules integral to chemical communication that would otherwise be markedly decreased prior to analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest:
The authors acknowledge the following potential conflicts of interest in companies pursuing open microfluidic technologies: EB: Tasso, Inc., Salus Discovery, LLC, and Stacks to the Future, LLC; ABT: Stacks to the Future, LLC. However, these companies are not related to the methods presented in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Cooper GM Signaling Molecules and Their Receptors. Cell Mol. Approach 2nd Ed. 2000.
-
- Zhao W; Oskeritzian CA; Pozez AL; Schwartz LB Cytokine Production by Skin-Derived Mast Cells: Endogenous Proteases Are Responsible for Degradation of Cytokines. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2005, 175 (4), 2635–2642. - PubMed
-
- Niwa Y; Akamatsu H; Sumi H; Ozaki Y; Abe A Evidence for Degradation of Cytokines in the Serum of Patients with Atopic Dermatitis by Calcium-Dependent Protease. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2000, 292 (8), 391–396. - PubMed
-
- Maddipati KR; Zhou S-L Stability and Analysis of Eicosanoids and Docosanoids in Tissue Culture Media. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2011, 94 (1), 59–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

