Retinal Physiology and Circulation: Effect of Diabetes
- PMID: 32941691
- PMCID: PMC10088460
- DOI: 10.1002/cphy.c190021
Retinal Physiology and Circulation: Effect of Diabetes
Abstract
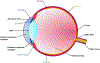
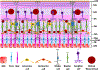
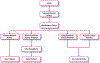
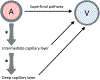
In this article, we present a discussion of diabetes and its complications, including the macrovascular and microvascular effects, with the latter of consequence to the retina. We will discuss the anatomy and physiology of the retina, including aspects of metabolism and mechanisms of oxygenation, with the latter accomplished via a combination of the retinal and choroidal blood circulations. Both of these vasculatures are altered in diabetes, with the retinal circulation intimately involved in the pathology of diabetic retinopathy. The later stages of diabetic retinopathy involve poorly controlled angiogenesis that is of great concern, but in our discussion, we will focus more on several alterations in the retinal circulation occurring earlier in the progression of disease, including reductions in blood flow and a possible redistribution of perfusion that may leave some areas of the retina ischemic and hypoxic. Finally, we include in this article a more recent area of investigation regarding the diabetic retinal vasculature, that is, the alterations to the endothelial surface layer that normally plays a vital role in maintaining physiological functions. © 2020 American Physiological Society. Compr Physiol 10:933-974, 2020.
Copyright © 2020 American Physiological Society. All rights reserved.
Figures


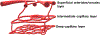

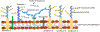
References
-
- Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet 352: 837–853, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Retinal Conditions - Common Eye Disorders∣Vision Health Initiative (VHI)∣. http://www.cdc.gov/visionhealth/basic_information/eye_disorders_retinal.htm: The Vision Health Initiative (VHI), 2014.
-
- Abu El-Asrar AM, Desmet S, Meersschaert A, Dralands L, Missotten L, Geboes K. Expression of the inducible isoform of nitric oxide synthase in the retinas of human subjects with diabetes mellitus. American journal of ophthalmology 132: 551–556, 2001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

