Optimization and clinical validation of dual-target RT-LAMP for SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32941977
- PMCID: PMC7490281
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2020.113972
Optimization and clinical validation of dual-target RT-LAMP for SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
A novel reverse-transcriptase loop mediated amplification (RT-LAMP) method targeting genes encoding the Spike (S) protein and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) of SARS-CoV-2 has been developed. The LAMP assay achieves a comparable limit of detection (25-50 copies per reaction) to commonly used RT-PCR protocols using clinical samples quantified by digital droplet PCR. Precision, cross-reactivity, inclusivity, and limit of detection studies were performed according to regulatory standards. Clinical validation of dual-target RT-LAMP (S and RdRP gene) achieved a PPA of 98.48 % (95 % CI 91.84%-99.96%) and NPA 100.00 % (95 % CI 93.84%-100.00%) based on the E gene and N2 gene reference RT-PCR methods. The method has implications for development of point of care technology using isothermal amplification.
Keywords: Assay; Covid; Diagnostics; LAMP; Molecular; PCR; SARS-CoV-2; Validation.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no declarations of interest. CD is an employee of Illucidx Inc. ANM and DRP have patents filed related to LAMP technology.
Figures
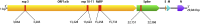

References
-
- 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/rt-pcr-panel-primer-probes.... Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

