Recent Advances in Understanding, Diagnosing, and Treating Hepatitis B Virus Infection
- PMID: 32942584
- PMCID: PMC7565763
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms8091416
Recent Advances in Understanding, Diagnosing, and Treating Hepatitis B Virus Infection
Abstract
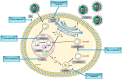
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection affects 292 million people worldwide and is associated with a broad range of clinical manifestations including cirrhosis, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Despite the availability of an effective vaccine HBV still causes nearly 900,000 deaths every year. Current treatment options keep HBV under control, but they do not offer a cure as they cannot completely clear HBV from infected hepatocytes. The recent development of reliable cell culture systems allowed for a better understanding of the host and viral mechanisms affecting HBV replication and persistence. Recent advances into the understanding of HBV biology, new potential diagnostic markers of hepatitis B infection, as well as novel antivirals targeting different steps in the HBV replication cycle are summarized in this review article.
Keywords: HBV; HBV RNA; HBcrAg; direct-acting antivirals; novel viral markers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . Global Hepatitis Report, 2017. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017.
-
- Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association The guidelines of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B (2019 version) Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2019;27:938–961. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2019.12.007. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

