Prevalence and characteristics of older adults with a persistent death wish without severe illness: a large cross-sectional survey
- PMID: 32943009
- PMCID: PMC7495831
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-020-01735-0
Prevalence and characteristics of older adults with a persistent death wish without severe illness: a large cross-sectional survey
Abstract
Background: Some older persons develop a persistent death wish without being severely ill, often referred to as "completed life" or "tiredness of life". In the Netherlands and Belgium, the question whether these persons should have legal options for euthanasia or physician-assisted suicide (EAS) is intensely debated. Our main aim was to investigate the prevalence and characteristics of older adults with a persistent death wish without severe illness, as the lack of this knowledge is a crucial problem in de debate.
Methods: We conducted a survey among a representative sample of 32,477 Dutch citizens aged 55+, comprising questions about health, existential issues and the nature of the death wish. Descriptive statistics were used to describe the group with a persistent death wish and no severe illness (PDW-NSI) and several subgroups.
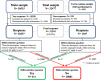
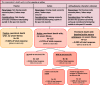
Results: A total of 21,294 respondents completed the questionnaire (response rate 65.6%). We identified 267 respondents (1.25%) as having a persistent death wish and no severe illness (PDW-NSI). PDW-NSI did not only occur among the oldest old. Although qualifying themselves as "not severely ill", those with PDW-NSI reported considerable health problems. A substantial minority of the PDW-NSI-group reported having had a death wish their whole lives. Within the group PDW-NSI 155 (0.73%) respondents had an active death wish, of which 36 (0.17% of the total response) reported a wish to actually end their lives. Thus, a death wish did not always equal a wish to actually end one's life. Moreover, the death wishes were often ambiguous. For example, almost half of the PDW-NSI-group (49.1%) indicated finding life worthwhile at this moment.
Conclusions: The identified characteristics challenge the dominant "completed life" or "tiredness of life" image of healthy persons over the age of 75 who, overseeing their lives, reasonably decide they would prefer to die. The results also show that death wishes without severe illness are often ambiguous and do not necessarily signify a wish to end one's life. It is of great importance to acknowledge these nuances and variety in the debate and in clinical practice, to be able to adequately recognize the persons involved and tailor to their needs.
Keywords: Completed life; Death wish; End-of-life; Euthanasia; Physician-assisted suicide; Suicide ideation; Tiredness of life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Freeman M. When the story's over. In: Andrews M, Sclater DS, Squire C, Treacher A, editors. Lines of narrative: psychosocial perspectives London. New York: Routledge; 2000.
-
- Schnabel P, Meyboom-de Jong B, Schudel W, Cleiren C, Mevis P, Verkerk M, et al. Voltooid leven: Over hulp bij zelfdoding aan mensen die hun leven voltooid achten [Completed life: On assisted suicide to people who consider their lives complete]. Adviescommissie voltooid leven; 2016. Report No.: 9082495201.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

