Meta-analysis of contrast-enhanced ultrasound and contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasound for the diagnosis of gallbladder malignancy
- PMID: 32943025
- PMCID: PMC7499977
- DOI: 10.1186/s12911-020-01252-5
Meta-analysis of contrast-enhanced ultrasound and contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasound for the diagnosis of gallbladder malignancy
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: Meta-analysis of contrast-enhanced ultrasound and contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasound for the diagnosis of gallbladder malignancy.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2022 Jun 7;22(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12911-022-01895-6. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2022. PMID: 35672739 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The diagnosis between benign and malignant gallbladder lesions is sometimes difficult. The objective of this study is to assess whether contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) and contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasound (CH-EUS) can be an accurate method for detecting gallbladder malignancy and to determine which imaging signs can be indicative of malignancy.
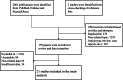
Methods: A study search of PubMed, Elsevier, and Sciencedirect was performed in May 2019. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve were used to examine the accuracy of CEUS and CH-EUS.
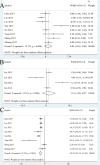
Results: Twenty-one studies were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled sensitivities of CEUS and CH-EUS were 0.81 (0.75-0.86) and 0.92 (0.86-0.95); the specificities were 0.94 (0.90-0.96) and 0.89 (0.69-0. 97); the DORs were 64 (32-127) and 89 (22-354); and the area under the SROC curves were 0.90 (0.87-0.92) and 0.92 (0.90-0.94). On CEUS, the diagnostic criterion for gallbladder malignancy according to four features were analyzed. Sensitivity and specificity were 0.75 (0.65-0.83) and 0.98 (0.85-1.00) for integrity of gallbladder wall; 0.69 (0.55-0.81) and 0.89 (0.77-0.95) for heterogeneous enhancement; 0.81 (0.71-0.88) and 0.88 (0.76-0.94) for irregular vessels; and 0.81 (0.66-0.91) and 0.75 (0.59-0.86) for washout time within 28 s. On CH-EUS, heterogeneous enhancement could be indicative of malignant lesions with a sensitivity of 0.94 (0.85-0.97); and the specificity was 0.92 (0.71-0.98).
Conclusions: CEUS and CH-EUS are promising and reliable imaging modalities with a high sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of gallbladder malignancy. CH-EUS might be more sensitive than CEUS with a higher sensitivity. In addition, irregular tralesional vessels and washout time within 28 s on CEUS and heterogeneous enhancement on CH-EUS are indicative of malignancy. However, larger scale and well-designed studies are warranted to verify our results.
Keywords: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound; Diagnosis; Endoscopic ultrasonography; Gallbladder; Malignant lesions; Meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Balfe DM, Ralls PW, Bree RL, Disantis DJ, Glick SN, Levine MS, et al. Imaging strategies in the initial evaluation of the jaundiced patient. American College of Radiology. ACR Appropriateness Criteria. Radiology. 2000;215(Suppl):125–133. - PubMed
-
- Xie X, Xu H, Xie X, Lu M, Kuang M, Xu Z. Differential diagnosis between benign and malignant gallbladder diseases with real-time contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Eur Radiol. 2010;20(1):239–248. - PubMed
-
- Runner GJ, Corwin MT, Siewert B, Eisenberg RL. Gallbladder wall thickening. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;202(1):W1–W12. - PubMed
-
- Giovannini M. Contrast-enhanced and 3-dimensional endoscopic ultrasonography. Gastroenterol Clin N Am. 2010;39(4):845–858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

