CLPTM1L induces estrogen receptor β signaling-mediated radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells
- PMID: 32943060
- PMCID: PMC7499972
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-020-00571-4
CLPTM1L induces estrogen receptor β signaling-mediated radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells
Abstract
Introduction: Radioresistance is a major challenge in lung cancer radiotherapy, and new radiosensitizers are urgently needed. Estrogen receptor β (ERβ) is involved in the progression of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), however, the role of ERβ in the response to radiotherapy in lung cancer remains elusive. In the present study, we investigated the mechanism underlying ERβ-mediated transcriptional activation and radioresistance of NSCLC cells.
Methods: Quantitative real-time PCR, western blot and immunohistochemistry were used to detect the expression of CLPTM1L, ERβ and other target genes. The mechanism of CLPTM1L in modulation of radiosensitivity was investigated by chromatin immunoprecipitation assay, luciferase reporter gene assay, immunofluorescence staining, confocal microscopy, coimmunoprecipitation and GST pull-down assays. The functional role of CLPTM1L was detected by function assays in vitro and in vivo.
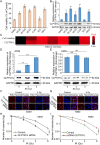
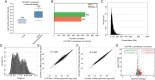
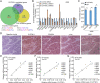
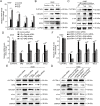
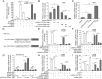
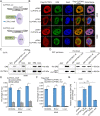
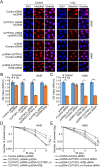
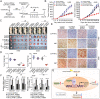
Results: CLPTM1L expression was negatively correlated with the radiosensitivity of NSCLC cell lines, and irradiation upregulated CLPTM1L in radioresistant (A549) but not in radiosensitive (H460) NSCLC cells. Meanwhile, IR induced the translocation of CLPTM1L from the cytoplasm into the nucleus in NSCLC cells. Moreover, CLPTM1L induced radioresistance in NSCLC cells. iTRAQ-based analysis and cDNA microarray identified irradiation-related genes commonly targeted by CLPTM1L and ERβ, and CLPTM1L upregulated ERβ-induced genes CDC25A, c-Jun, and BCL2. Mechanistically, CLPTM1L coactivated ERβ by directly interacting with ERβ through the LXXLL NR (nuclear receptor)-binding motif. Functionally, ERβ silencing was sufficient to block CLPTM1L-enhanced radioresistance of NSCLC cells in vitro. CLPTM1L shRNA treatment in combination with irradiation significantly inhibited cancer cell growth in NSCLC xenograft tumors in vivo.
Conclusions: The present results indicate that CLPTM1L acts as a critical coactivator of ERβ to promote the transcription of its target genes and induce radioresistance of NSCLC cells, suggesting a new target for radiosensitization in NSCLC therapy. Video Abstract.
Keywords: CLPTM1L; ERβ; Non-small cell lung cancer; Radioresistance; Radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-365 enhances the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells through targeting CDC25A.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Apr 30;512(2):392-398. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.03.082. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 30902389
-
ITGB1 enhances the Radioresistance of human Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells by modulating the DNA damage response and YAP1-induced Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Jan 18;17(2):635-650. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.52319. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33613118 Free PMC article.
-
SOX2 Promotes Radioresistance in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer by Regulating Tumor Cells Dedifferentiation.Int J Med Sci. 2023 Apr 29;20(6):781-796. doi: 10.7150/ijms.75315. eCollection 2023. Int J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37213675 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular and Cellular Strategies of Glioblastoma and Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells Conferring Radioresistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 5;23(21):13577. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113577. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy-related signaling pathways in non-small cell lung cancer.Mol Cell Biochem. 2022 Feb;477(2):385-393. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04280-5. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 34757567 Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear receptors as novel regulators that modulate cancer radiosensitivity and normal tissue radiotoxicity.Mol Cancer. 2025 May 30;24(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02362-2. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40442680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of microRNA-494 in tumor progression.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Nov 15;15(11):6342-6361. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 38074823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cleft lip and palate transmembrane protein 1-like is a putative regulator of tumorigenesis and sensitization of cervical cancer cells to cisplatin.Front Oncol. 2024 Sep 13;14:1440906. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1440906. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39346724 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogens, Cancer and Immunity.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 30;14(9):2265. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092265. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen receptor beta promotes lung cancer invasion via increasing CXCR4 expression.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Jan 21;13(1):70. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04514-4. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35064116 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

