Intravenous methylprednisolone pulse as a treatment for hospitalised severe COVID-19 patients: results from a randomised controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 32943404
- PMCID: PMC7758541
- DOI: 10.1183/13993003.02808-2020
Intravenous methylprednisolone pulse as a treatment for hospitalised severe COVID-19 patients: results from a randomised controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Introduction: There are no determined treatment agents for severe COVID-19. It is suggested that methylprednisolone, as an immunosuppressive treatment, can reduce the inflammation of the respiratory system in COVID-19 patients.
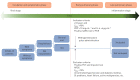
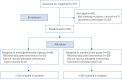
Methods: We conducted a single-blind, randomised controlled clinical trial involving severe hospitalised patients with confirmed COVID-19 at the early pulmonary phase of the illness in Iran. The patients were randomly allocated in a 1:1 ratio by the block randomisation method to receive standard care with methylprednisolone pulse (intravenous injection, 250 mg·day-1 for 3 days) or standard care alone. The study end-point was the time of clinical improvement or death, whichever came first. Primary and safety analysis was done in the intention-to-treat (ITT) population.
Results: 68 eligible patients underwent randomisation (34 patients in each group) from April 20, 2020 to June 20, 2020. In the standard care group, six patients received corticosteroids by the attending physician before the treatment and were excluded from the overall analysis. The percentage of improved patients was higher in the methylprednisolone group than in the standard care group (94.1% versus 57.1%) and the mortality rate was significantly lower in the methylprednisolone group (5.9% versus 42.9%; p<0.001). We demonstrated that patients in the methylprednisolone group had a significantly increased survival time compared with patients in the standard care group (log-rank test: p<0.001; hazard ratio 0.293, 95% CI 0.154-0.556). Two patients (5.8%) in the methylprednisolone group and two patients (7.1%) in the standard care group showed severe adverse events between initiation of treatment and the end of the study.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that methylprednisolone pulse could be an efficient therapeutic agent for hospitalised severe COVID-19 patients at the pulmonary phase.
Copyright ©ERS 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: M. Edalatifard has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M. Akhtari has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M. Salehi has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: Z. Naderi has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A. Jamshidi has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: S. Mostafaei has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: S.R. Najafizadeh has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: E. Farhadi has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: N. Jalili has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M. Esfahani has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: B. Rahimi has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: H. Kazemzadeh has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M. Mahmoodi Aliabadi has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: T. Ghazanfari has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M. Sattarian has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: H. Ebrahimi Louyeh has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: S.R. Raeeskarami has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: S. Jamalimoghadamsiahkali has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: N. Khajavirad has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M. Mahmoudi has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A. Rostamian has nothing to disclose.
Figures

Comment in
-
Pandemic trials: evidence-based medicine on steroids.Eur Respir J. 2020 Dec 24;56(6):2004116. doi: 10.1183/13993003.04116-2020. Print 2020 Dec. Eur Respir J. 2020. PMID: 33361452 Free PMC article.
-
Is high-dose glucocorticoid beneficial in COVID-19?Eur Respir J. 2021 Apr 15;57(4):2100065. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00065-2021. Print 2021 Apr. Eur Respir J. 2021. PMID: 33509962 Free PMC article.
-
Corticosteroids in COVID-19: one size does not fit all.Eur Respir J. 2021 Apr 15;57(4):2100224. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00224-2021. Print 2021 Apr. Eur Respir J. 2021. PMID: 33574071 Free PMC article.
-
Reply: Is high-dose glucocorticoid beneficial in COVID-19?Eur Respir J. 2021 Apr 15;57(4):2100324. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00324-2021. Print 2021 Apr. Eur Respir J. 2021. PMID: 33602862 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
