Phase Ib Study of Chemoprevention with Green Tea Polyphenon E and Erlotinib in Patients with Advanced Premalignant Lesions (APL) of the Head and Neck
- PMID: 32943457
- PMCID: PMC8016407
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2276
Phase Ib Study of Chemoprevention with Green Tea Polyphenon E and Erlotinib in Patients with Advanced Premalignant Lesions (APL) of the Head and Neck
Abstract
Purpose: On the basis of synergistic effects between green tea polyphenon E (PPE) and EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor in preclinical studies, we conducted a phase Ib study of the PPE and erlotinib combination in patients with advanced premalignant lesions (APL) of the oral cavity and larynx.
Patients and methods: Patients were treated with a fixed dose of PPE (200 mg three times a day) and dose escalation of erlotinib (50, 75, 100 mg daily) for 6 months with tissue biopsy at baseline and 6 months. Primary endpoints were safety and toxicity; secondary endpoints were evaluation of pathologic response, cancer-free survival (CFS), overall survival (OS), and biomarker modulation.
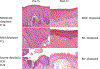
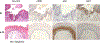
Results: Among 21 enrolled patients, 19 began treatment and 17 completed 6 months of treatment with PPE and erlotinib. Main characteristics of treated patients: 15 severe dysplasia or carcinoma in situ and 17 oral cavity. Only skin rash was associated with dose-limiting toxicity and MTD. Recommended doses for phase II studies are PPE 600 mg daily plus erlotinib 100 mg daily for 6 months. Pathologic responses in 17 evaluable patients: pathologic complete response (47%) and pathologic partial response (18%). The 5-year CFS and OS were 66.3% and 93%, respectively. Among tested biomarkers, only phosphorylated ERK was correlated with response to treatment.
Conclusions: Treatment with PPE and erlotinib combination was well tolerated in patients with APLs of the head and neck, and showed a high rate of pathologic response with excellent CFS. This combination deserves further investigation for the chemoprevention and/or prevention of second primary tumors in early-stage head and neck cancer.
©2020 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chemoprevention of head and neck cancer with celecoxib and erlotinib: results of a phase ib and pharmacokinetic study.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2014 Mar;7(3):283-91. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-13-0215. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2014. PMID: 24085777 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of the Safety and Pharmacokinetics of Pictilisib in Combination with Erlotinib in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors.Oncologist. 2017 Dec;22(12):1491-1499. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0090. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Oncologist. 2017. PMID: 28798270 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic study of panobinostat, an HDAC inhibitor, combined with erlotinib in patients with advanced aerodigestive tract tumors.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Mar 15;20(6):1644-55. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2235. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24429877 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of erlotinib (OSI-774) in combination with docetaxel in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SSCHN).Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011 Mar;67(3):579-86. doi: 10.1007/s00280-010-1332-y. Epub 2010 May 19. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20490801 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase II trial of erlotinib and docetaxel in advanced and refractory hepatocellular and biliary cancers: Hoosier Oncology Group GI06-101.Oncologist. 2012;17(1):13. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2011-0253. Epub 2011 Dec 30. Oncologist. 2012. PMID: 22210086 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Therapeutic Potential in Cancer: Mechanism of Action and Clinical Implications.Molecules. 2023 Jul 6;28(13):5246. doi: 10.3390/molecules28135246. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37446908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Substances of Natural Origin in Medicine: Plants vs. Cancer.Cells. 2023 Mar 23;12(7):986. doi: 10.3390/cells12070986. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37048059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemoprevention of Head and Neck Cancer: A Review of Current Approaches and Future Perspectives.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2024 Oct 1;17(10):443-455. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-24-0093. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2024. PMID: 38978394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Natural Products and Their Multitargeted Approach to Treat Solid Cancer.Cells. 2022 Jul 15;11(14):2209. doi: 10.3390/cells11142209. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35883653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress and Dietary Antioxidants in Head and Neck Cancer.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Apr 24;14(5):508. doi: 10.3390/antiox14050508. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427390 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Haddad RI, Shin DM. Recent advances in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(11):1143–54. - PubMed
-
- Hong WK, Endicott J, Itri LM, Doos W, Batsakis JG, Bell R, et al. 13-cis-retinoic acid in the treatment of oral leukoplakia. N Engl J Med. 1986;315(24):1501–5. - PubMed
-
- Lippman SM, Batsakis JG, Toth BB, Weber RS, Lee JJ, Martin JW, et al. Comparison of low-dose isotretinoin with beta carotene to prevent oral carcinogenesis. N Engl J Med. 1993;328(1):15–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

