COVID-19 and the heart: what we have learnt so far
- PMID: 32943474
- PMCID: PMC10016902
- DOI: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138284
COVID-19 and the heart: what we have learnt so far
Abstract
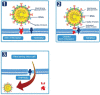
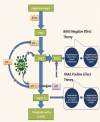
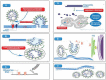
Since the outbreak of COVID-19 or coronavirus disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 from Wuhan, China, the cardiology fraternity's interest has been drawn towards the pandemic with a high case fatality rate of 10.5% and 6% in patients with heart disease and hypertension, respectively. One of the postulated mechanisms for this high fatality rate is the possible abundance of ACE type 2 receptor in the cardiovascular system that strongly binds with the spike protein of COVID-19 and helps internalise into the cell resulting in acute cardiac injury (ACI). More than 7% of cases with COVID-19 are reported to have this type of ACI. A tenfold rise in mortality has been observed in patients with COVID-19 who experience a rise in high-sensitivity (hs)-troponin. All most half of the patients who died of COVID-19 had a rise in hs-troponin. More than 15% of cases with COVID-19 experienced different types of arrhythmias. All these statistics denote how important cardiovascular pathology is in patients with COVID-19. Controversies of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors usage in patients with COVID-19 and meticulous handling of case with acute coronary syndrome categorically stresses cardiologists to bust the myths hovering around and set a standard guideline to counterfeit the fatality with timely diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19-induced ACI. In this review, we sought to summarise the current evidence of COVID-19-associated cardiac injury and suggest the implications for its proper diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: Angiotensin receptor blocker; Arrhythmias; COVID-19; Carditis; SARS-Cov-2.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Clerkin KJ, Fried JA, Raikhelkar J, et al. COVID-19 and cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2020;141:1648–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

