Long-term Cognitive, Psychological, and Health Outcomes Associated With Child Abuse and Neglect
- PMID: 32943535
- PMCID: PMC7786831
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2020-0438
Long-term Cognitive, Psychological, and Health Outcomes Associated With Child Abuse and Neglect
Abstract
Potential long-lasting adverse effects of child maltreatment have been widely reported, although little is known about the distinctive long-term impact of differing types of maltreatment. Our objective for this special article is to integrate findings from the Mater-University of Queensland Study of Pregnancy, a longitudinal prenatal cohort study spanning 2 decades. We compare and contrast the associations of specific types of maltreatment with long-term cognitive, psychological, addiction, sexual health, and physical health outcomes assessed in up to 5200 offspring at 14 and/or 21 years of age. Overall, psychological maltreatment (emotional abuse and/or neglect) was associated with the greatest number of adverse outcomes in almost all areas of assessment. Sexual abuse was associated with early sexual debut and youth pregnancy, attention problems, posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms, and depression, although associations were not specific for sexual abuse. Physical abuse was associated with externalizing behavior problems, delinquency, and drug abuse. Neglect, but not emotional abuse, was associated with having multiple sexual partners, cannabis abuse and/or dependence, and experiencing visual hallucinations. Emotional abuse, but not neglect, revealed increased odds for psychosis, injecting-drug use, experiencing harassment later in life, pregnancy miscarriage, and reporting asthma symptoms. Significant cognitive delays and educational failure were seen for both abuse and neglect during adolescence and adulthood. In conclusion, child maltreatment, particularly emotional abuse and neglect, is associated with a wide range of long-term adverse health and developmental outcomes. A renewed focus on prevention and early intervention strategies, especially related to psychological maltreatment, will be required to address these challenges in the future.
Copyright © 2020 by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
POTENTIAL CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors have indicated they have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
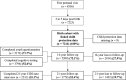

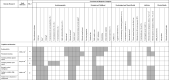





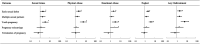
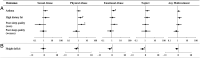
References
-
- Gilbert R, Widom CS, Browne K, Fergusson D, Webb E, Janson S. Burden and consequences of child maltreatment in high-income countries. Lancet. 2009;373(9657):68–81 - PubMed
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services; Administration for Children and Families; Administration on Children, Youth and Families; Children’s Bureau . Child Maltreatment 2017. Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office; 2019
-
- Jaffee SR. Child maltreatment and risk for psychopathology in childhood and adulthood. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2017;13:525–551 - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Report of the Consultation on Child Abuse Prevention, 29–31 March, 1999. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 1999
-
- Stoltenborgh M, Bakermans-Kranenburg MJ, Alink LRA, IJzendoorn MH. The prevalence of child maltreatment across the globe: review of a series of meta-analyses. Child Abuse Rev. 2015;24(1):37–50
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

