MiR-596 activated by EP300 controls the tumorigenesis in epithelial ovarian cancer by declining BRD4 and KPNA4
- PMID: 32943995
- PMCID: PMC7488530
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-020-01497-0
MiR-596 activated by EP300 controls the tumorigenesis in epithelial ovarian cancer by declining BRD4 and KPNA4
Abstract
Background: Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), a subclass of ovarian cancer (OC), is usually diagnosed at advanced stages due to the lack of effective screening means. Mounting reports have disclosed the vitally important roles of microRNAs (miRNAs) in carcinogenesis. Here, we aimed to find out possible miRNAs participating in EOC development.
Methods: qRT-PCR ad western blot respectively examined the mRNA and protein levels of studied genes. CCK-8, colony formation, flow cytometry, TUNEL and spheroid formation assays were appropriately employed for examining cell proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis and stemness. The interaction between molecules was affirmed by luciferase reporter, RNA pull down and ChIP assays.
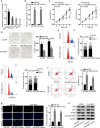
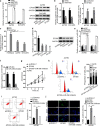
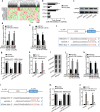
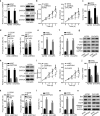
Results: In consistent with the observation of a past study, miR-596 expression was relatively low in EOC cells. Up-regulating miR-596 suppressed EOC cell proliferation and stemness. EP300 transcriptionally activated miR-596 to serve as a tumor-repressor in EOC. Then BRD4 and KPNA4, whose knockdown led to restraining effects on cell growth and stemness, were both revealed to be targeted by miR-596 in EOC. Lastly, rescue assays affirmed the tumor-restraining role of miR-596-BRD4/KPNA4 axis in EOC.
Conclusion: EP300-activated miR-596 hampered cell growth and stemness via targeting BRD4 and KPNA4 in EOC, proofing miR-596 as a promising therapeutic target in treating EOC patients.
Keywords: BRD4; EP300; Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC); KPNA4; miR-596.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-145 targets TRIM2 and exerts tumor-suppressing functions in epithelial ovarian cancer.Gynecol Oncol. 2015 Dec;139(3):513-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2015.10.008. Epub 2015 Oct 16. Gynecol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26472353
-
circCELSR1 facilitates ovarian cancer proliferation and metastasis by sponging miR-598 to activate BRD4 signals.Mol Med. 2020 Jul 8;26(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s10020-020-00194-y. Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32640974 Free PMC article.
-
miR-211 suppresses epithelial ovarian cancer proliferation and cell-cycle progression by targeting Cyclin D1 and CDK6.Mol Cancer. 2015 Mar 11;14:57. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0322-4. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25889927 Free PMC article.
-
Circ-PGAM1 promotes malignant progression of epithelial ovarian cancer through regulation of the miR-542-3p/CDC5L/PEAK1 pathway.Cancer Med. 2020 May;9(10):3500-3521. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2929. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32167655 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Ovarian Epithelial Carcinoma Tumorigenesis and Progression by microRNA 106b Mediated through the RhoC Pathway.PLoS One. 2015 May 1;10(5):e0125714. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125714. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25933027 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Systematic Characterization of the Clinical Relevance of KPNA4 in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 29;12:834728. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.834728. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35425701 Free PMC article.
-
Human Enzyme PADI4 Binds to the Nuclear Carrier Importin α3.Cells. 2022 Jul 11;11(14):2166. doi: 10.3390/cells11142166. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35883608 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of BRD4 isoforms long (BRD4-L) and short (BRD4-S) promotes chemotherapy resistance in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma.Genes Cancer. 2023 Sep 12;14:56-76. doi: 10.18632/genesandcancer.233. eCollection 2023. Genes Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37705995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115–132. - PubMed
-
- Goff BA, Mandel L, Muntz HG, Melancon CH. Ovarian carcinoma diagnosis. Cancer. 2000;89(10):2068–2075. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–297. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

