Effect of milk fat-based infant formulae on stool fatty acid soaps and calcium excretion in healthy term infants: two double-blind randomised cross-over trials
- PMID: 32944265
- PMCID: PMC7489008
- DOI: 10.1186/s40795-020-00365-4
Effect of milk fat-based infant formulae on stool fatty acid soaps and calcium excretion in healthy term infants: two double-blind randomised cross-over trials
Abstract
Background: Palmitic acid (PA) is predominantly esterified at the SN-2 position of triacylglycerols in human milk. PA at the SN-2 position is more efficiently absorbed and results in reduced formation of PA soaps, as well as reduced fatty acid (FA) and calcium malabsorption. Bovine milk fat (MF), a natural source of SN-2-palmitate, was used in the fat blend of infant formulae (IF) in the current study to investigate its effect on stool fatty acid soaps, calcium excretion and stool characteristics.
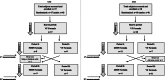
Methods: Two double-blind, randomised cross-over trials (CS1, CS2) were conducted in parallel with healthy term, formula-fed infants aged 9-14 weeks. After a two-week run-in period, infants in CS1 (n = 17) were randomly allocated to receive either a 50% MF-based formula (50MF) or a 100% vegetable fat (VF) formula; in CS2 (n = 18), infants received either a 20% MF-based formula (20MF) or the VF formula, in a 2 × 2-week cross-over design. At the end of each two-week intervention period, stool samples were collected for FA, FA soaps and calcium excretion analysis and stool consistency was assessed according to the Amsterdam Infant Stool Scale (AISS).
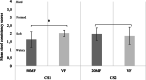
Results: MF-based groups showed no significant difference in PA in stools compared to VF group, although reduced stool PA soaps (CS1: 111.28 ± 18.33 vs. 220.25 ± 29.35 mg/g dry weight, p < 0.0001; CS2: 216.24 ± 25.16 vs. 233.94 ± 35.12 mg/g dry weight, p = 0.0023), total FA soaps and calcium excretion (CS1: 46.40 ± 5.27 vs. 49.88 ± 4.77 mg/g dry weight, p = 0.0041; CS2: 46.20 ± 4.26 vs. 50.47 ± 6.71 mg/g dry weight, p = 0.0067) were observed. Furthermore, the 50MF group showed a favourable lower mean stool consistency score compared to the VF group (1.64 ± 0.49 vs. 2.03 ± 0.19, p = 0.0008).
Conclusions: While the use of bovine MF in IF did not affect PA concentrations in stool, lower excretion of palmitate soaps, total FA soaps and calcium was seen in healthy term infants. 50MF formula also showed improved stool consistency. The use of MF in IF could be an interesting approach to improve gut comfort and stool characteristics in infants, warranting further research.
Trial registration: Netherlands Trial Registry Identifier: NTR6702. Date registered: December 01, 2017.
Keywords: Amsterdam infant stool scale; Calcium excretion; Milk fat; Palmitate soap; SN-2-palmitate; Stool consistency.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsITV, MMV, PP and RB are employees at FrieslandCampina. Any opinions, findings, conclusions or recommendations expressed in the current study are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of FrieslandCampina. The other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of bovine milk fat-based infant formulae on microbiota, metabolites and stool parameters in healthy term infants in a randomized, crossover, placebo-controlled trial.BMC Nutr. 2022 Aug 29;8(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s40795-022-00575-y. BMC Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36038938 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of an Infant Formula Containing a Novel Fat Blend (Cow's Milk Fat, Fish and Vegetable Oil) and Prebiotics on Stool Fatty Acid Soaps and Erythrocyte Fatty Acid Profiles in Full-Term Healthy Newborns.Ann Nutr Metab. 2021;77(3):138-145. doi: 10.1159/000515705. Epub 2021 Apr 30. Ann Nutr Metab. 2021. PMID: 33934094 Clinical Trial.
-
Stool fatty acid soaps, stool consistency and gastrointestinal tolerance in term infants fed infant formulas containing high sn-2 palmitate with or without oligofructose: a double-blind, randomized clinical trial.Nutr J. 2014 Nov 5;13:105. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-13-105. Nutr J. 2014. PMID: 25373935 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Importance of the regiospecific distribution of long-chain saturated fatty acids on gut comfort, fat and calcium absorption in infants.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2017 Jun;121:40-51. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2017.05.007. Epub 2017 Jun 4. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2017. PMID: 28651696 Review.
-
Effects of Sn-2-palmitate-enriched formula feeding on infants' growth, stool characteristics, stool fatty acid soap contents and bone mineral content: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(30):10256-10266. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2079606. Epub 2022 May 27. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 35622955
Cited by
-
A Scoping Review of Clinical Studies in Infants Fed Formulas Containing Palm Oil or Palm Olein and Sn-2 Palmitate.J Nutr. 2021 Oct 1;151(10):2997-3035. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxab246. J Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34510181 Free PMC article.
-
A cross-sectional study on stool- and gastrointestinal-related outcomes of Mexican infants consuming different formulae.BMC Pediatr. 2023 Dec 15;23(1):634. doi: 10.1186/s12887-023-04426-y. BMC Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 38102583 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of calcium palmitate on bacteria associated with infant gut microbiota.Microbiologyopen. 2021 Jun;10(3):e1187. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.1187. Microbiologyopen. 2021. PMID: 34180592 Free PMC article.
-
Feeding infant formula with low sn-2 palmitate causes changes in newborn's intestinal environments through an increase in fecal soaped palmitic acid.PLoS One. 2025 May 28;20(5):e0324256. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324256. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40435194 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Partly Replacing Vegetable Fat with Bovine Milk Fat in Infant Formula on Postprandial Lipid and Energy Metabolism: A Proof-of-principle Study in Healthy Young Male Adults.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2021 May;65(9):e2000848. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202000848. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2021. PMID: 33682997 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
