Lung cancer in women in 21th century
- PMID: 32944353
- PMCID: PMC7475544
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-20-287
Lung cancer in women in 21th century
Abstract
Lung cancer is the first cause of death from malignant disease. The distressing epidemiological data show the increasing female to male incidence ratio for this tumor. A high incidence of lung cancer in never smokers with importance of environmental agents makes a problem among women. Adenocarcinoma (ADC) is noted in women with increasing rate and ethnic background impacts female lung cancer with differences in the incidence of genetic aberrations. The conception of different hormonal status is taken into consideration as potential explanation of variant cancer biology and clinical manifestation in women and men. The impact of 17-β-estradiol, estrogen receptors, aromatase expression, pituitary sex hormones receptors in carcinogenesis with relation between estrogens and genetic aberrations are investigated. The response to newest therapies among female is also different than in men. This overview summarizes currently available evidence on the specificity of female lung cancer and presents the direction of necessary studies.
Keywords: EGFR mutation; Lung cancer; adenocarcinoma (ADC); estrogen; women.
2020 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/jtd-20-287). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
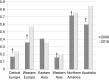
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
