An isoflavone derivative potently inhibits the angiogenesis and progression of triple-negative breast cancer by targeting the MTA2/SerRS/VEGFA pathway
- PMID: 32944400
- PMCID: PMC7476100
- DOI: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0010
An isoflavone derivative potently inhibits the angiogenesis and progression of triple-negative breast cancer by targeting the MTA2/SerRS/VEGFA pathway
Abstract
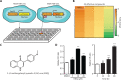
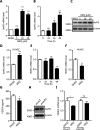
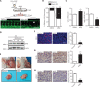
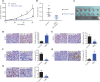
Objective: Angiogenesis plays a vital role in tumor growth and metastasis. Here, we aimed to find novel efficient antiangiogenic molecules targeting vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA ) at the transcriptional level to treat triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Methods: We used a cell-based seryl tRNA synthetase (SerRS) promoter-driven dual-luciferase reporter system to screen an in-house library of 384 naturally occurring small molecules and their derivatives to find candidate molecules that could upregulate the expression of SerRS, a potent transcriptional repressor of VEGFA. The levels of SerRS and VEGFA were examined by quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR), western blotting, and/or ELISAs in TNBC cells after candidate molecule administration. Zebrafish, the Matrigel plug angiogenesis assay in mice, the TNBC allograft, and xenograft mouse models were used to evaluate the in vivo anti-angiogenic and anti-cancer activities. Furthermore, the potential direct targets of the candidates were identified by proteomics and biochemical studies. Results: We found the most active compound was 3-(4-methoxyphenyl) quinolin-4(1H)-one (MEQ), an isoflavone derivative. In TNBC cells, MEQ treatment resulted in increased SerRS mRNA (P < 0.001) and protein levels and downregulated VEGFA production. Both the vascular development of zebrafish and Matrigel plug angiogenesis in mice were inhibited by MEQ. MEQ also suppressed the angiogenesis in TNBC allografts and xenografts in mice, resulting in inhibited tumor growth and prolonged overall survival (P < 0.05). Finally, we found that MEQ regulated SerRS transcription by interacting with MTA2 (Metastasis Associated 1 Family Member 2). Conclusions: Our findings suggested that the MTA2/SerRS/VEGFA axis is a drug-treatable anti-angiogenic target, and MEQ is a promising anti-tumor molecule that merits further investigation for clinical applications.
Keywords: Isoflavone; MTA2; SerRS; VEGFA; tumor angiogenesis.
Copyright: © 2020, Cancer Biology & Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Herb-sourced emodin inhibits angiogenesis of breast cancer by targeting VEGFA transcription.Theranostics. 2020 May 22;10(15):6839-6853. doi: 10.7150/thno.43622. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32550907 Free PMC article.
-
Emodin combined with 5-aminolevulinic acid photodynamic therapy inhibits condyloma acuminate angiogenesis by targeting SerRS.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Oct;28(19):e70122. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70122. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39351642 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of seryl-tRNA synthetase by ATM/ATR is essential for hypoxia-induced angiogenesis.PLoS Biol. 2020 Dec 22;18(12):e3000991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000991. eCollection 2020 Dec. PLoS Biol. 2020. PMID: 33351793 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking the ATR-SerRS-VEGFA pathway targets angiogenesis for UV-induced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.Mol Carcinog. 2024 Jun;63(6):1160-1173. doi: 10.1002/mc.23716. Epub 2024 May 2. Mol Carcinog. 2024. PMID: 38695641
-
VEGFA and tumour angiogenesis.J Intern Med. 2013 Feb;273(2):114-27. doi: 10.1111/joim.12019. J Intern Med. 2013. PMID: 23216836 Review.
Cited by
-
Bladder Cancer-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Promote Tumor Angiogenesis by Inducing HBP-Related Metabolic Reprogramming and SerRS O-GlcNAcylation in Endothelial Cells.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Oct;9(30):e2202993. doi: 10.1002/advs.202202993. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 36045101 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-Protein Interactions of Seryl-tRNA Synthetases with Emphasis on Human Counterparts and Their Connection to Health and Disease.Life (Basel). 2024 Jan 15;14(1):124. doi: 10.3390/life14010124. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38255739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal EPHA2 derived from highly metastatic breast cancer cells promotes angiogenesis by activating the AMPK signaling pathway through Ephrin A1-EPHA2 forward signaling.Theranostics. 2022 May 13;12(9):4127-4146. doi: 10.7150/thno.72404. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35673569 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of VEGF-A expression and VEGF-A-targeted therapy in malignant tumors.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Apr 30;150(5):221. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05714-5. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38687357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[JAG1 promotes migration, invasion, and adhesion of triple-negative breast cancer cells by promoting angiogenesis].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022 Jul 20;42(7):1100-1108. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.07.21. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35869777 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Warburg O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science. 1956;123:309–14. - PubMed
-
- DeSantis CE, Ma J, Goding Sauer A, Newman LA, Jemal A. Breast cancer statistics, 2017, racial disparity in mortality by state. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:439–48. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Waks AG, Winer EP. Breast cancer treatment: a review. J Am Med Assoc. 2019;321:288–300. - PubMed
-
- Ismail-Khan R, Bui MM. A review of triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Control. 2010;17:173–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
