TRPV1 expressed throughout the arterial circulation regulates vasoconstriction and blood pressure
- PMID: 32944976
- PMCID: PMC8565923
- DOI: 10.1113/JP279909
TRPV1 expressed throughout the arterial circulation regulates vasoconstriction and blood pressure
Abstract
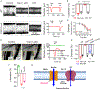
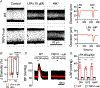
Key points: The functional roles of the capsaicin receptor, TRPV1, outside of sensory nerves are unclear. We mapped TRPV1 in the mouse circulation, revealing extensive expression in the smooth muscle of resistance arterioles supplying skeletal muscle, heart and adipose tissue. Activation of TRPV1 in vascular myocytes constricted arteries, reduced coronary flow in isolated hearts and increased systemic blood pressure. These functional effects were retained after sensory nerve ablation, indicating specific signalling by arterial TRPV1. TRPV1 mediated the vasoconstrictive and blood pressure responses to the endogenous inflammatory lipid lysophosphatidic acid. These results show that TRPV1 in arteriolar myocytes modulates regional blood flow and systemic blood pressure, and suggest that TRPV1 may be a target of vasoactive inflammatory mediators.
Abstract: The capsaicin receptor, TRPV1, is a key ion channel involved in inflammatory pain signalling. Although mainly studied in sensory nerves, there are reports of TRPV1 expression in isolated segments of the vasculature, but whether the channel localizes to vascular endothelium or smooth muscle is controversial and the distribution and functional roles of TRPV1 in arteries remain unknown. We mapped functional TRPV1 expression throughout the mouse arterial circulation. Analysis of reporter mouse lines TRPV1PLAP-nlacZ and TRPV1-Cre:tdTomato combined with Ca2+ imaging revealed specific localization of TRPV1 to smooth muscle of terminal arterioles in the heart, adipose tissue and skeletal muscle. Capsaicin evoked inward currents (current density ∼10% of sensory neurons) and raised intracellular Ca2+ levels in arterial smooth muscle cells, constricted arterioles ex vivo and in vivo and increased systemic blood pressure in mice and rats. Further, capsaicin markedly and dose-dependently reduced coronary flow. Pharmacological and/or genetic disruption of TRPV1 abolished all these effects of capsaicin as well as vasoconstriction triggered by lysophosphatidic acid, a bioactive lipid generated by platelets and atherogenic plaques. Notably, ablation of sensory nerves did not affect the responses to capsaicin revealing a vascular smooth muscle-restricted signalling mechanism. Moreover, unlike in sensory nerves, TRPV1 function in arteries was resistant to activity-induced desensitization. Thus, TRPV1 activation in vascular myocytes enables a persistent depolarizing current, leading to constriction of coronary, skeletal muscle and adipose arterioles and a sustained increase in systemic blood pressure.
Keywords: TRPV1; blood pressure; capsaicin; lysophosphatidic acid; vascular smooth muscle.
© 2020 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2020 The Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
T.P. and G.A. are co-inventors of a provisional patent application related to technology presented in this article.
Figures








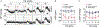

Similar articles
-
TRPV1 in arteries enables a rapid myogenic tone.J Physiol. 2022 Apr;600(7):1651-1666. doi: 10.1113/JP281873. Epub 2022 Feb 1. J Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35020949 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of age and exercise training on coronary microvascular smooth muscle phenotype and function.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018 Jan 1;124(1):140-149. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00459.2017. Epub 2017 Oct 12. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018. PMID: 29025901 Free PMC article.
-
Nociceptive transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) in sensory neurons are targets of the antifungal drug econazole.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2024 Aug 21;25(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s40360-024-00779-x. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39169383 Free PMC article.
-
Automated devices for identifying peripheral arterial disease in people with leg ulceration: an evidence synthesis and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Aug;28(37):1-158. doi: 10.3310/TWCG3912. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39186036 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Targeting TRPV1 for Cancer Pain Relief: Can It Work?Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 2;16(3):648. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030648. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resiniferatoxin: Nature's Precision Medicine to Silence TRPV1-Positive Afferents.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 10;24(20):15042. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015042. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soft wireless sternal patch to detect systemic vasoconstriction using photoplethysmography.iScience. 2023 Feb 13;26(3):106184. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106184. eCollection 2023 Mar 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 36879814 Free PMC article.
-
Capsaicin and TRPV1 Channels in the Cardiovascular System: The Role of Inflammation.Cells. 2021 Dec 22;11(1):18. doi: 10.3390/cells11010018. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of transient receptor potential channels in the regulation of vascular tone.Drug Discov Today. 2024 Jul;29(7):104051. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2024.104051. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Drug Discov Today. 2024. PMID: 38838960 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baluk P (1997). Neurogenic inflammation in skin and airways. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc 2, 76–81. - PubMed
-
- Bratz IN, Dick GM, Tune JD, Edwards JM, Neeb ZP, Dincer UD & Sturek M (2008). Impaired capsaicin-induced relaxation of coronary arteries in a porcine model of the metabolic syndrome. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294, H2489–H2496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

