A novel DNA primase-helicase pair encoded by SCC mec elements
- PMID: 32945259
- PMCID: PMC7581432
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.55478
A novel DNA primase-helicase pair encoded by SCC mec elements
Abstract
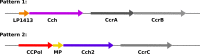
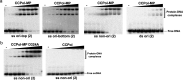
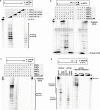
Mobile genetic elements (MGEs) are a rich source of new enzymes, and conversely, understanding the activities of MGE-encoded proteins can elucidate MGE function. Here, we biochemically characterize three proteins encoded by a conserved operon carried by the Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome (SCCmec), an MGE that confers methicillin resistance to Staphylococcus aureus, creating MRSA strains. The first of these proteins, CCPol, is an active A-family DNA polymerase. The middle protein, MP, binds tightly to CCPol and confers upon it the ability to synthesize DNA primers de novo. The CCPol-MP complex is therefore a unique primase-polymerase enzyme unrelated to either known primase family. The third protein, Cch2, is a 3'-to-5' helicase. Cch2 additionally binds specifically to a dsDNA sequence downstream of its gene that is also a preferred initiation site for priming by CCPol-MP. Taken together, our results suggest that this is a functional replication module for SCCmec.
Keywords: A-family polymerase; SCCmec; Staphylococcus aureus; biochemistry; chemical biology; helicase; mobile genetic elements; primase.
© 2020, Bebel et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AB, MW, IM, PR No competing interests declared
Figures


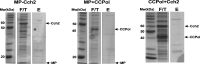










References
-
- Abramoff MD, Magalhães PJ, Ram SJ. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics International. 2007;13:36–42.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

