Hepatic tumors: pitfall in diagnostic imaging
- PMID: 32945274
- PMCID: PMC7944669
- DOI: 10.23750/abm.v91i8-S.9969
Hepatic tumors: pitfall in diagnostic imaging
Abstract
On computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), hepatocellular tumors are characterized based on typical imaging findings. However, hepatocellular adenoma, focal nodular hyperplasia, and hepatocellular carcinoma can show uncommon appearances at CT and MRI, which may lead to diagnostic challenges. When assessing focal hepatic lesions, radiologists need to be aware of these atypical imaging findings to avoid misdiagnoses that can alter the management plan. The purpose of this review is to illustrate a variety of pitfalls and atypical features of hepatocellular tumors that can lead to misinterpretations providing specific clues to the correct diagnoses.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare that they have no commercial associations (e.g. consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangement etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Figures

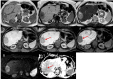

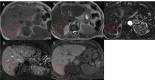
References
-
- Mazzei MA, Squitieri NC, Sani E, et al. Differences in perfusion CT parameter values with commercial software upgrades: a preliminary report about algorithm consistency and stability. Acta Radiol. 2013;54:805–11. - PubMed
-
- Hori M, Murakami T, Kim T, Tomoda K, Nakamura H. CT Scan and MRI in the Differentiation of Liver Tumors. Dig Dis. 2004;22:39–55. - PubMed
-
- Pesapane F, Patella F, Fumarola EM, et al. Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) Diffusion Weighted Imaging (DWI) in the Periferic Prostate Cancer Detection and Stratification. Med Oncol. 2017;34:35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

