De novo transcriptome analysis and gene expression profiling of fish scales isolated from Carassius auratus during space flight: Impact of melatonin on gene expression in response to space radiation
- PMID: 32945420
- PMCID: PMC7466330
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11363
De novo transcriptome analysis and gene expression profiling of fish scales isolated from Carassius auratus during space flight: Impact of melatonin on gene expression in response to space radiation
Abstract
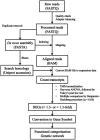
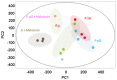
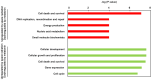
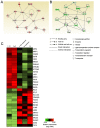
Astronauts are inevitably exposed to two major risks during space flight, microgravity and radiation. Exposure to microgravity has been discovered to lead to rapid and vigorous bone loss due to elevated osteoclastic activity. In addition, long‑term exposure to low‑dose‑rate space radiation was identified to promote DNA damage accumulation that triggered chronic inflammation, resulting in an increased risk for bone marrow suppression and carcinogenesis. In our previous study, melatonin, a hormone known to regulate the sleep‑wake cycle, upregulated calcitonin expression levels and downregulated receptor activator of nuclear factor‑κB ligand expression levels, leading to improved osteoclastic activity in a fish scale model. These results indicated that melatonin may represent a potential drug or lead compound for the prevention of bone loss under microgravity conditions. However, it is unclear whether melatonin affects the biological response induced by space radiation. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effect of melatonin on the expression levels of genes responsive to space radiation. In the present study, to support the previous data regarding de novo transcriptome analysis of goldfish scales, a detailed and improved experimental method (e.g., PCR duplicate removal followed by de novo assembly, global normalization and calculation of statistical significance) was applied for the analysis. In addition, the transcriptome data were analyzed via global normalization, functional categorization and gene network construction to determine the impact of melatonin on gene expression levels in irradiated fish scales cultured in space. The results of the present study demonstrated that melatonin treatment counteracted microgravity‑ and radiation‑induced alterations in the expression levels of genes associated with DNA replication, DNA repair, proliferation, cell death and survival. Thus, it was concluded that melatonin may promote cell survival and ensure normal cell proliferation in cells exposed to space radiation.
Keywords: space radiation; transcriptome; de novo assembly; fish scale; gene network; melatonin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Melatonin is a potential drug for the prevention of bone loss during space flight.J Pineal Res. 2019 Oct;67(3):e12594. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12594. Epub 2019 Jul 19. J Pineal Res. 2019. PMID: 31286565 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of sclerostin in the regenerating scales of goldfish and its increase under microgravity during space flight.Biomed Res. 2020;41(6):279-288. doi: 10.2220/biomedres.41.279. Biomed Res. 2020. PMID: 33268672
-
Induced Torpor as a Countermeasure for Low Dose Radiation Exposure in a Zebrafish Model.Cells. 2021 Apr 14;10(4):906. doi: 10.3390/cells10040906. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33920039 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological consequences of space flight, including abnormal bone metabolism, space radiation injury, and circadian clock dysregulation: Implications of melatonin use and regulation as a countermeasure.J Pineal Res. 2023 Jan;74(1):e12834. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12834. Epub 2022 Oct 17. J Pineal Res. 2023. PMID: 36203395 Review.
-
Brains in space: impact of microgravity and cosmic radiation on the CNS during space exploration.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2025 Jun;26(6):354-371. doi: 10.1038/s41583-025-00923-4. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40247135 Review.
Cited by
-
Glyoxal-induced formation of advanced glycation end-products in type 1 collagen decreases both its strength and flexibility in vitro.J Diabetes Investig. 2021 Sep;12(9):1555-1559. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13528. Epub 2021 Mar 11. J Diabetes Investig. 2021. PMID: 33605082 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin in animal husbandry: functions and applications.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Sep 2;11:1444578. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1444578. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39286597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin as the Cornerstone of Neuroimmunoendocrinology.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 6;23(3):1835. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031835. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic response to low‑intensity ultrasound on mouse ST2 bone marrow stromal cells.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Mar;23(3):173. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11812. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33398373 Free PMC article.
-
Genes involved in osteogenic differentiation induced by low‑intensity pulsed ultrasound in goldfish scales.Biomed Rep. 2024 Nov 22;22(2):18. doi: 10.3892/br.2024.1896. eCollection 2025 Feb. Biomed Rep. 2024. PMID: 39651404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hellweg CE, Dilruba S, Adrian A, Feles S, Schmitz C, Berger T, Przybyla B, Briganti L, Franz M, Segerer J, et al. Space experiment ‘Cellular Responses to Radiation in Space (CellRad)’: Hardware and biological system tests. Life Sci Space Res (Amst) 2015;7:73–89. doi: 10.1016/j.lssr.2015.10.003. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

