Ginsenoside Rg3 enhances the anticancer effect of 5‑FU in colon cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway
- PMID: 32945504
- PMCID: PMC7448421
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2020.7728
Ginsenoside Rg3 enhances the anticancer effect of 5‑FU in colon cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway
Abstract
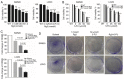
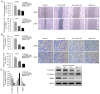
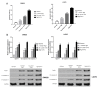
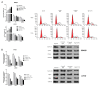
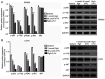
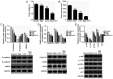
Chemotherapy is one of the most commonly used treatments for patients with advanced colon cancer, yet the toxicity of chemotherapy agents, such as 5‑fluorouracil (5‑FU), limits the effectiveness of chemotherapy. Ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3) is an active ingredient isolated from ginseng. Rg3 has been shown to display anticancer effects on a variety of malignancies. Yet, whether Rg3 synergizes the effect of 5‑FU to inhibit the growth of human colon cancer remains unknown. The present study was designed to ascertain whether Rg3 is able to enhance the anti‑colon cancer effect of 5‑FU. The results revealed that combined treatment of Rg3 and 5‑FU significantly enhanced the inhibition of the proliferation, colony formation, invasion and migration of human colon cancer cells (SW620 and LOVO) in vitro. We also found that combined treatment of Rg3 and 5‑FU significantly enhanced the apoptosis of colon cancer cells by activating the Apaf1/caspase 9/caspase 3 pathway and arrested the cell cycle of the colon cancer cells in G0/G1 by promoting the expression of Cyclin D1, CDK2 and CDK4. In addition, the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in colon cancer cells was suppressed by Rg3 and 5‑FU. In vivo, Rg3 synergized the effect of 5‑FU to inhibit the growth of human colon cancer xenografts in nude mice. Similarly, combined treatment of Rg3 and 5‑FU altered the expression of colon cancer protein in vivo and in vitro. Collectively, the present study demonstrated that ginsenoside Rg3 enhances the anticancer effect of 5‑FU in colon cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway.
Keywords: ginsenoside Rg3; colon cancer; 5-fluorouracil; PI3K/AKT.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Melatonin synergizes the chemotherapeutic effect of 5-fluorouracil in colon cancer by suppressing PI3K/AKT and NF-κB/iNOS signaling pathways.J Pineal Res. 2017 Mar;62(2). doi: 10.1111/jpi.12380. Epub 2016 Dec 24. J Pineal Res. 2017. PMID: 27865009
-
Ginsenoside Rg3 enhances the anti-proliferative activity of erlotinib in pancreatic cancer cell lines by downregulation of EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Dec;96:619-625. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.043. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 29035827
-
Inhibiting PI3K-AKt signaling pathway is involved in antitumor effects of ginsenoside Rg3 in lung cancer cell.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jan;85:16-21. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.11.096. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 27930981
-
Ginsenoside Rg3 enhances the anticancer effects of 5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer and reduces drug resistance and the Hedgehog pathway activation.Arab J Gastroenterol. 2024 Nov;25(4):437-443. doi: 10.1016/j.ajg.2024.09.003. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Arab J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39500672
-
Synergistic anticancer activity of 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg3 and Sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating PTEN/Akt signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jan;97:1282-1288. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.006. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29156516
Cited by
-
Transformation of Ginsenosides by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum MB11 Fermentation: Minor Ginsenosides Conversion and Enhancement of Anti-Colorectal Cancer Activity.Molecules. 2023 Dec 20;29(1):27. doi: 10.3390/molecules29010027. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38202610 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of ginseng in the treatment of gastrointestinal cancers.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 12;13:1036498. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1036498. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36313365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knockdown of SNORA47 Inhibits the Tumorigenesis of NSCLC via Mediation of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 19;11:620213. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.620213. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33816250 Free PMC article.
-
Ginsenoside Rg3: A Review of its Anticancer Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Applications.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(10):869-884. doi: 10.2174/0115680266283661240226052054. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38441023 Review.
-
Natural anti-cancer products: insights from herbal medicine.Chin Med. 2025 Jun 9;20(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01124-y. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40490812 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;60:277–300. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

