Upregulation of serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 exacerbates brain injury and neurological deficits after cardiac arrest
- PMID: 32946263
- PMCID: PMC8083081
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00399.2020
Upregulation of serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 exacerbates brain injury and neurological deficits after cardiac arrest
Abstract
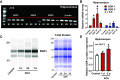
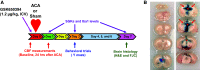
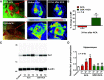
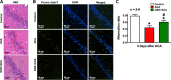
Cardiopulmonary arrest (CA) is the leading cause of death and disability in the United States. CA-induced brain injury is influenced by multifactorial processes, including reduced cerebral blood flow (hypoperfusion) and neuroinflammation, which can lead to neuronal cell death and functional deficits. We have identified serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase-1 (SGK1) as a new target in brain ischemia previously described in the heart, liver, and kidneys (i.e., diabetes and hypertension). Our data suggest brain SGK1 mRNA and protein expression (i.e., hippocampus), presented with hypoperfusion (low cerebral blood flow) and neuroinflammation, leading to further studies of the potential role of SGK1 in CA-induced brain injury. We used a 6-min asphyxia cardiac arrest (ACA) rat model to induce global cerebral ischemia. Modulation of SGK1 was implemented via GSK650394, a SGK1-specific inhibitor (1.2 μg/kg icv). Accordingly, treatment with GSK650394 attenuated cortical hypoperfusion and neuroinflammation (via Iba1 expression) after ACA, whereas neuronal survival was enhanced in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. Learning/memory deficits were observed 3 days after ACA but ameliorated with GSK650394. In conclusion, SGK1 is a major contributor to ACA-induced brain injury and neurological deficits, while inhibition of SGK1 with GSK650394 provided neuroprotection against CA-induced hypoperfusion, neuroinflammation, neuronal cell death, and learning/memory deficits. Our studies could lead to a novel, therapeutic target for alleviating brain injury following cerebral ischemia.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Upregulation of SGK1 exacerbates brain injury during cerebral ischemia. Inhibition of SGK1 affords neuroprotection against cardiac arrest-induced hypoperfusion, neuroinflammation, neuronal cell death, and neurological deficits.
Keywords: cerebral blood flow; cerebral ischemia; neuroinflammation; neuronal cell death; serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of serum/glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 in brain function following cerebral ischemia.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024 Jul;44(7):1145-1162. doi: 10.1177/0271678X231224508. Epub 2024 Jan 18. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024. PMID: 38235747 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of serum and glucocorticoid regulated kinases by GSK650394 reduced infarct size in early cerebral ischemia-reperfusion with decreased BBB disruption.Neurosci Lett. 2021 Sep 25;762:136143. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2021.136143. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Neurosci Lett. 2021. PMID: 34332027 Free PMC article.
-
The protective effects of gallic acid and SGK1 inhibitor on cardiac damage and genes involved in Ca2+ homeostasis in an isolated heart model of ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Jul;397(7):5207-5217. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-02949-4. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38252301
-
Serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 (SGK1) as an emerging therapeutic target for cardiac diseases.Pharmacol Res. 2024 Oct;208:107369. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107369. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Pharmacol Res. 2024. PMID: 39209082 Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of serum and glucocorticoid inducible kinase inhibition.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2013 Jun;22(6):701-14. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2013.778971. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23506284 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein arginine methyltransferase 8 modulates mitochondrial bioenergetics and neuroinflammation after hypoxic stress.J Neurochem. 2021 Nov;159(4):742-761. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15462. Epub 2021 Aug 25. J Neurochem. 2021. PMID: 34216036 Free PMC article.
-
The role of SGK1 in neurologic diseases: A friend or foe?IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024 Dec 6;17:503-512. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2024.12.003. eCollection 2024 Dec. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39737082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of Neuropeptide Y2 Receptor Can Inhibit Global Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Brain Injury.Neuromolecular Med. 2022 Jun;24(2):97-112. doi: 10.1007/s12017-021-08665-z. Epub 2021 May 21. Neuromolecular Med. 2022. PMID: 34019239 Free PMC article.
-
Serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase 1 (SGK1) in neurological disorders: pain or gain.Exp Neurol. 2024 Dec;382:114973. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114973. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Exp Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39326820 Review.
-
The role of serum/glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 in brain function following cerebral ischemia.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024 Jul;44(7):1145-1162. doi: 10.1177/0271678X231224508. Epub 2024 Jan 18. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024. PMID: 38235747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anacker C, Cattaneo A, Musaelyan K, Zunszain PA, Horowitz M, Molteni R, Luoni A, Calabrese F, Tansey K, Gennarelli M, Thuret S, Price J, Uher R, Riva MA, Pariante CM. Role for the kinase SGK1 in stress, depression, and glucocorticoid effects on hippocampal neurogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110: 8708–8713, 2013. doi:10.1073/pnas.1300886110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

